
Two Shot & Multi Shot Injection Molding - 1 2 plastic molding
Author:gly Date: 2024-10-15
At Integrated Molding Solutions, we deliver precision plastic injection molded parts to your door. IMS provides innovative plastic solutions offering guidance and help for small and large businesses alike.
When comparing plastic material fillers, glass fiber is the most common to use for injection molding. Glass fibers provide reinforced strength and low density for a reasonable cost. Carbon fibers are a more expensive filler but can be used as a colorant, pigment, UV barrier, and antioxidant. Not only do carbon fibers reinforce the strength of the plastic, but they provide excellent resistance to creep, break stress, fatigue, and corrosive environments. Many companies in the automotive industry use carbon fiber fillers to produce lightweight parts because of the strength and durability it adds to plastic. Another plastic material filler we use at Integrated Molding Solutions is talc. Combining talc with polypropylene greatly increases the stiffness and heat resistance while reducing mold shrinkage and cycle time. Talc is also less abrasive than glass and can provide a better surface for finishing.
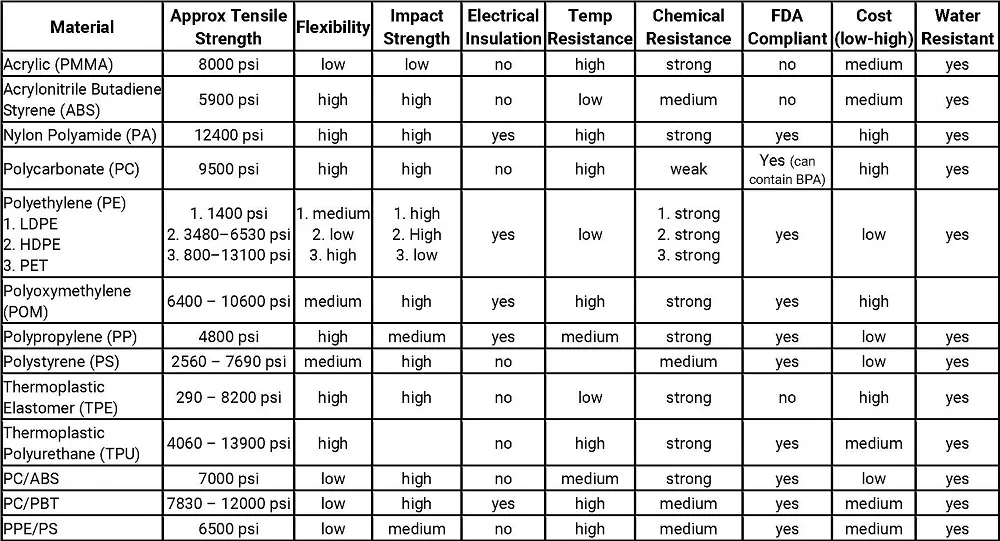
There are several important properties to consider for selecting injection molding materials for any plastic product. These include the desired tensile strength, flexural modulus (bending stiffness), Izod impact (toughness), electrical insulation, temperature resistance, chemical resistance, FDA compliance, and cost of the final product.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) – ABS is another amorphous thermoplastic with a low melting point. As an opaque polymer, ABS is compatible with colorants and has multiple options for various textures and surface finishes. Known for its strength and impact resistance, ABS however has weak resistance to UV rays, weather, high friction, and solvents, and it generates heavy smoke when burned, but this can be fixed with additives. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is best used for electronic components and coverings, as well as automotive components, consumer goods, and sports equipment.
Another property to consider when selecting your plastic material is the material’s flexibility or bending stiffness. Also known as flexural modulus, the material’s stiffness is measured in psi. Next, is electrical insulation properties, or dielectric strength. Typically measured in volts per micrometer (v/mil), to determine how well the plastic part will prevent the flow of electrical charge. While these are accurate for certain standards, sometimes we have to use metric units due to the material info we are given, or doing tests in other standards (ISO or DIN for example).
How the injection molding material reacts to heat is important to consider when comparing thermoplastic materials. The thermal properties will determine the max and min working temperature, the melting temperature, and can determine how the material will react in the mold and as it cools. Injection molding pressure and flow rate of material can cause shrinkage and dimensional instability if not chosen carefully.
Insert molding is a systematic process of modeling thermoplastic material around an additional component. Most pliable thermoplastic resins are suitable for the insert molding process. The added piece is often a metal part. The main advantage of mold-in inserts is that generic threaded inserts are readily available in standard sizes. Generic inserts help keep costs down and avoid further customization costs. Metal inserts provide properties that plastic alone wears down over time, such as threading.
Mechanical fasteners have the distinct advantage of offering disassembly and reassembly. Components include screws, nuts, bolts, rivets, pins, and inserts are examples of mechanical fasteners. Tapping is a process used to place threading inside a plastic injection molded hole. Advantages mechanical fasteners provide are a stronger, longer-lasting bond, durability, and disassembly. When you need to ensure the strength of the hold, mechanical fasteners are likely the correct choice.
Electroplating or electro-deposition is a process whereby a metal material coats the surface of a part. In the electroplating process, a permanent bond connects the metal to the surface of another piece. The process involves an electrolyte or plating bath charged with electricity. The electricity-charged bath deposits small particles of the metal over the part’s surface. Therefore, this process effectively coats the plastic piece in a completely shiny, smooth metal finish.
If you need to increase the material’s strength without sacrificing other properties, the addition of fillers can be a perfect solution. Glass, carbon, and talc are the three most common fillers to achieve an increase in stiffness and strength. By combining our material with the selected filler, we create a custom material consisting of 5%-60% filler. The higher percentage of filler used, the more the surface quality of the final product will be affected.
Nylon Polyamide (PA) – Polyamide, otherwise known as nylon, is a synthetic material. Nylons’ high-temperature resistance does make it prone to shrinkage and inadequate filling of the mold. It can be degraded by sunlight and has poor resistance to strong acids and bases, but additives and fillers can help with these shortcomings. Best for snap-fit closures like caps, plastic threaded inserts, casings, gears, and electrical connectors.
Heat staking is another permanent bonding technique. This bonding concept takes advantage of the base material being malleable plastic. The base material is heated up and the plastic reformed using a combination of heat and pressure to model the plastic around the second piece forming a hardware-free bond. One advantage is that we can use it to combine two alike or dissimilar materials. Also, it is a reasonably easy bonding process that does not require any additional parts or materials.
Polyoxymethylene (POM) – Polyoxymethylene, commonly known as acetal, is a low friction, high stiffness, general purpose semicrystalline thermoplastic. The engineered thermoplastic has low water absorption, good chemical resistance, and demonstrates excellent dimensional stability. There are two types of POM plastics: homopolymers and copolymers, with the differences lying within their dimensional stability and creep resistance, whereas a copolymer does better over time in both categories. Due to its low friction, the most common products made with injection molding polyoxymethylene are metal replacement parts like bearings, gears, conveyor belts, screws, and more.
The first property to consider when selecting injection molding materials is the product’s desired tensile strength. Tensile strength is the resistance to being pulled apart, typically measured in PSI (pounds per square inch). Similarly, another material property to consider is Izod impact (notched) or toughness. The Izod impact test is an ASTM standard method of determining the impact resistance of materials. This is done by swinging an arm into the notched sample, recording the energy required to break the part, which is measured in ft·lb/in2.
Electronics are still a leading sector in the use of plastic resin parts. Plastics do not conduct electricity. Electronics often need plastics to insulate the electricity running through them. Consequently, a plastic part can make the perfect insulator for electronics and electrical devices. Plastics also have a lower conductivity for heat. Meaning, that plastics do not transfer heat well due to their insulating properties. This particular property works to the advantage of the plastics industry when it wishes to shield heat from other more delicate parts or the user. You may also treat plastics with special flame retardant finishing applications to further support their fire-resistant properties.
Plastic can be found in just about every consumer product or used in almost every industry in some shape and form. Electronics, consumer products, automotive, healthcare, and even aerospace all use plastic materials to make endless parts all with different functions and specifications. Therefore, plastic material selection is one of the most important steps when manufacturing any plastic product. At Integrated Molding Solutions, we always review and consult on injection molding materials selection before undertaking any project. In this article, IMS shares our decades of plastic industry knowledge, in this injection molding materials selection guide.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) – Thermoplastic Polyurethane is a type of TPE but can be injection molded into a harder rubber with its high durometer. TPU is highly popular due to its ability to handle extreme temperatures and its resistance to chemicals, oils, and abrasion. It comes in commercial, medical, and industrial grades, making it great for medical devices, electronic casings, shoes, consumer goods, and wheels.
The automotive industry is controlling fuel efficiency by switching to lightweight plastics. Using plastics for many auto parts reduces the vehicle’s overall weight and increases fuel efficiency. With the need for better fuel economy solutions, the automotive business has turned to plastics manufacturing for many automotive components. Additionally, government regulations recently are pressing the automotive industry to move from iron and steel to plastics. This push from the government is shifting the automotive industry towards higher-grade plastics in place of metals. The recent drive for a plastic manufacturing process in the automotive segment allows us to anticipate that injection molded plastics will increase rapidly under these new regulations.
Polystyrene (PS) – Another commodity plastic is polystyrene. This amorphous thermoplastic plastic resin can be broken down into two basic types: general-purpose polystyrene (GPPS) and high-impact polystyrene (HIPS). GPPS is known as crystal-clear polystyrene but is prone to cracking. HIPS has a more matte finish and is not transparent but is the stronger of the two. Polystyrene thermoplastics are inexpensive, lightweight, and resistant to moisture and gamma radiation, making them excellent to sterilize medical devices. While injection molded PS is recyclable it is non-biodegradable. Polystyrene is best suited for injection molding medical, optical, and electronic plastic parts, but is also used to injection mold some consumer goods.
Lastly, cost is important for obvious reasons and can change in numerous ways, from availability, and material properties, to the use of material additives. If multiple plastic materials will meet your property requirements then cost may be the determining factor to produce your product to your specifications.
Polycarbonate (PC) – Polycarbonate is a strong and lightweight amorphous thermoplastic with good transparency. 250 times stronger than glass, polycarbonate still has uniform mold shrinkage making it easy to use for injection molding. However, PC contains BPA, so not recommended for food prep or storage. When colored, polycarbonate retains its strength. Therefore, polycarbonate thermoplastic is best used for consumer goods or housing products.
Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Thermoplastic elastomer is a blend of rubber and plastic materials, so it performs like rubber but is processed like plastic and is more recyclable. It has shorter mold cycles and supports two-shot injection molding, making it easier and less expensive to mold than rubber. TPE can lose rubber properties at high temperatures, but it’s the best plastic material for impact resistance. TPE could be used for footwear, auto parts, pet products, and medical applications like breathing tubes, ventilation masks, and catheters.
Additives can affect plastic parts in various ways. Simple modifications like changing the thermoplastics color, to manipulating the properties to provide self-lubricating or anti-static capabilities. Another example is the addition of foaming agents to turn polystyrene into Styrofoam. With additives, we can create a car bumper to withstand the impact of an accident, or an airplane component that can handle creep resistance from its usage cycle.
There are two types of thermoplastic materials that we commonly use at Integrated Molding Solutions, amorphous and semicrystalline. Amorphous thermoplastic material can be highly transparent and has good formability with a lower melting temperature range. While amorphous thermoplastics have poor chemical resistance, this provides an easier bond to other materials using adhesives or solvents.
On the other hand, semicrystalline thermoplastic material has great fatigue and stress cracking resistance making it the perfect material for bearing and wear. However, semicrystalline thermoplastic material can have high chemical resistance and difficulty bonding to other parts using adhesives or solvents.
When comparing plastic materials, use this plastic materials comparison chart to identify which injection molding materials will meet the product specifications. One of the many benefits of working with a professional plastic fabrication company is their knowledge of plastic material alloys, fillers, and additives. Custom plastic injection molding materials can be engineered to meet required product properties that common plastic molding materials cannot.
If you are still unable to find a plastic material with the properties to meet your product’s specifications, there is a final alternative. Integrated Molding Solutions will work with you to engineer the perfect injection molding material combined with additives. Additives manipulate the plastic material’s properties without as large of a material composition percent change as using fillers.
Acrylic (PMMA) – Acrylic, also known as poly(methyl methacrylate), is an amorphous thermoplastic. It’s good for structural applications due to its formability and ability to form tight tolerances with injection molding. Acrylic is clear and strong, making it a great, lightweight alternative for glass. Also, PMMA resists sunlight and will not degrade from water, making it perfect for outdoor windows and as a transparent enclosure.
These two forms of painting apply color to the part. The painting application is ideal after molding. Painting can be any color or even metallic finishes painted over plastic. This application also helps with particular requirements such as non-static parts. In comparison, pad printing permanently places an image onto the components. Pad printing is similar in nature to a rubber stamp. An inverted image is coated with paint and laid against the part to transfer the image to the part’s surface.
Integrated Molding has decades of plastic manufacturing experience. Let us guide you from concept through design, mold creation, material selection, production, parts assembly, to finished product. Join us in our mission to provide environmentally responsible plastic products to grow businesses and leave a positive impact on the world.
PC/PBT – PC/PBT is an alloy consisting of one amorphous thermoplastic (polycarbonate) and one semicrystalline thermoplastic (polybutylene terephthalate). An engineering polymer that has good chemical resistance, temperature resistance, and mechanical strength, PC/PBT is typically used for insulating components in electronics and the electricity industry.
Tapping and threading make for easy disassembly. Both processes produce threads on a part. “Threads” means a small threadlike ridge or groove. Tapping and threading both create threaded surfaces. The threading process makes threads on the outside surface. Like a bolt or screw, for example. Similarly, tapping creates threads inside a hole, such as a nut. Threading is performed with a die tool, while tapping uses a tapping tool. When opposite features come together, the threads interlock.
Polyethylene (PE) – Polyethylene is a consumer-grade polymer that can be selected by density making it globally, the most commonly used plastic. Three main types of polyethylene are high density (HDPE), low density (LDPE), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET, PETE). Polyethylene is a low-cost plastic material that has high resistance to chemicals and moisture. PE plastics are best used to injection mold larger items therefore they are frequently used for blow molding films and bottles.
PC/ABS – An alloy combination of Polycarbonate and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. PC/ABS provides a strong, stiff, and heat-resistant alloy, taking the best properties of these two amorphous thermoplastics. Its low shrinkage lowers the chance of injection molding defects making it perfect for components in electronics or automotive industries.

Polypropylene (PP) This semicrystalline thermoplastic is the second most commonly used plastic in the world for its flexibility. It is very similar to polyethylene but slightly harder and more heat-resistant. When used in injection molding, it can be recycled multiple times and blended with other plastic materials very well. However, polypropylene is extremely flammable (fixed with flame retardant additives), and difficult to bond – which also means it’s one of the materials that is harder to paint or fasten. With its low density, this commodity plastic is best used for sporting goods, power tools, living hinges for plastic bottles, and storage containers.
Plastics are a growing industry that is becoming prominent in the healthcare sector. The medical industry is establishing a foothold in plastic 3D printing as a modern solution. Plastic molds help doctors to see a CT scan in 3D physically. The dental occupation often uses 3D plastic molds to custom fit parts before surgery. Research suggests that Medical grade polymers used in healthcare will positively impact growth in the medical field over the next decade.
Ultraviolet (UV) bonding is another permanent bonding process. The ultraviolet bonding process carries the advantage of bonding plastics to other materials such as glass, ceramic, and metal. Bonding using ultraviolet light is a highly intense concentration of ultraviolet lighting that instantly dries or cures the adhesive. Moreover, UV bonding works in seconds to bond plastic components with other materials. A solid bond forming in moments lessens production time and often reduces rates.
Chemical resistance is also important because this will determine how well the plastic can resist being degraded by certain chemicals better than others. For example, gasoline will melt polystyrene (basically making napalm), but not polyethylene (which plastic gas cans are made of). Therefore, it is important to identify what the finished product will come in contact with and pick a compatible material. Along this note, FDA compliance is an important factor when dealing with medical or consumer products that must be approved for human contact.
GETTING A QUOTE WITH LK-MOULD IS FREE AND SIMPLE.
FIND MORE OF OUR SERVICES:


Plastic Molding

Rapid Prototyping

Pressure Die Casting

Parts Assembly



