
The Difference Between Extrusion Molding vs Injection ... - extrusion and inject
Author:gly Date: 2024-10-15
Let’s explore the over moulding and insert moulding processes in detail and understand the benefits of using these plastic injection moulding methods
By exploring resources such as the blog “How Does an Injection Moulding Machine Work?“, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the steps involved in plastic injection moulding.
Additives are often mixed with plastic resin during the injection moulding process and coatings are added to the moulded component as part of the finishing process.
Plastic polymer materials used for plastic injection moulding are called thermoplastics because they become molten when heated but harden again when cooled. The mould design, properties required for the finished component and its function will determine thermoplastic selection.
The modern manufacturing landscape demands adaptability and efficiency. Enter low-volume injection molding as the solution for on-demand manufacturing. Companies can order custom parts tailored to their exact specifications, whether it’s specific shapes, materials, or unique features. This flexibility minimizes excess inventory, streamlines production, and ultimately leads to significant cost savings.
Low-volume injection molding isn’t merely a modern manufacturing process; it’s a pathway to innovation, cost-effectiveness, and quality. It empowers businesses to bring their ideas to life swiftly, respond to market demands, and deliver products that meet the highest standards. As you start your manufacturing projects, consider the immense potential of low-volume injection molding.
Draft angles are essential for ensuring that the molded part can be easily removed from the mold without damaging it. All vertical faces should have at least 0.5 degrees of draft, but if the part design allows, it’s preferable to have 2 to 3 degrees of draft. In some cases, complex surfaces may even require as much as 5 degrees of draft. These draft angles facilitate smooth ejection of the part from the mold, reducing the risk of defects and ensuring a successful molding process.
Insert moulding is often required to add strength and functional elements to a product. The components that are inserted are usually made from metal such as threaded screws that will allow the finished product to be firmly held together with the fewest parts possible.
Thermoforming, particularly vacuum forming, is a viable option for thinner parts with simpler designs. It’s a cost-effective method for creating parts with larger surface areas.
Low-volume injection molding is a vital tool in the realm of rapid prototyping. Designers and engineers can swiftly transform the concepts into tangible prototypes. It enables thorough testing, design tweaks, and refinements, ensuring that the final product meets or exceeds expectations. In today’s competitive market, being the first to market with a high-quality product is often the key to success, and low-volume molding plays a pivotal role in achieving that goal.
2K or 2-shot moulding is sometimes also called twin shot or double injection moulding. This process can produce complicated parts by blending two completely different types of thermoplastic. It is different to overmoulding because it involves controlling the injection of the different materials in one cycle which is an automated process requiring specialist 2-shot moulding machines.
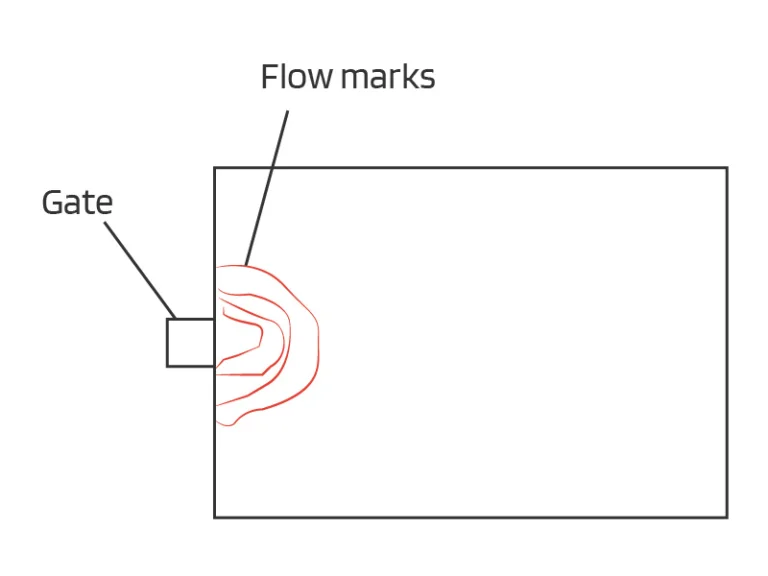
Injection molding flow marks are a common injection molding defect. While flow marks generally do not influence the structural integrity
Low volume injection molding is an ideal solution for businesses needing specialized, custom plastic or rubber parts in smaller quantities. Low volume plastic mold production for specialized parts allows manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in design or demand without significant upfront investments. In this engineer’s guide to low volume injection molding, we’ll explore the key benefits and considerations of using low volume production molds for both plastic and rubber components.
Incorporate rounded edges and corners whenever possible. Sharp angles can be challenging to mold and may lead to part defects.
3D printing offers the advantage of creating parts with highly complex geometries that may not be achievable through other manufacturing methods. It’s especially popular for prototyping.
Clean room moulding is used for producing plastic parts in a climate-controlled and sterile environment to avoid the risk of contamination from dust and other particles. This is important for certain industries such as medical, precision electronics, aerospace and defence. Cleanroom injection moulding applications include medical device housings, dental products, surgical equipment, fluid delivery containers, semi-conductors and advanced electronics.
High Performance Polymers – such as polyketones, polysulfones (PPSU), polyarylates, polyamides, and liquid crystal polymers (LCP) such as PEEK are characterised by a combination of high modulus, melting points (greater than 250°C), biocompatibility, electrical insulation and low-friction surfaces.
There are several reasons why the injection moulding process is popular for producing plastic parts. Simply put, it enables uniform, consistent, high-quality parts to be made in large volumes, within relatively short timeframes and with low material waste which contributes to a low overall part cost. Due to the accuracy and ability to produce complex geometries, there is also little need for finishing once the part has been successfully ejected from the mould.
Owen Greenings & Mumford Ltd is the trading name of OGM Ltd, a company registered in England and Wales with company number 00742307
Plastic injection moulding is a highly adaptable manufacturing technique that enables efficient production of diverse plastic parts and components in large quantities. The process involves introducing plastic pellets into a heated chamber through a hopper. Inside the chamber, the plastic undergoes melting, blending, and is subsequently propelled under pressure (injected) into a metallic mould. As the molten plastic fills the mould, it rapidly cools and solidifies, assuming the precise shape of the intended component.
Injection, dwelling and cooling – plastic pellets or granules are fed into a hopper where they are mixed with additives, fillers and pigments. These are then transported through a barrel by a reciprocating screw and heated to form hot, melted plastic resin. This is then injected through a nozzle into the cavity of the mould tool where it starts to cool and harden to form the shape of the component.
Additives include pigments, glass or carbon fibres for strength and stainless-steel fibres for controlling electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radiofrequency interference (RFI). Fillers such as clay or talc may also be added to improve hardness of the finished product or reduce warpage during the injection moulding process.
Too thick can lead to cooling issues, while too thin can result in structural weaknesses. It’s important to consider the appropriate wall thickness to avoid issues like warping or sink marks during the cooling process. Ideally, wall thicknesses should typically stay within the range of 0.04 to 0.14 inches (1 to 3.5mm). Thicker walls can lead to cooling inconsistencies and potential defects, while thinner walls may result in structural weaknesses. Striking the right balance in wall thickness is essential for producing high-quality molded parts.
Zhongde as one of low volume injection molding companies, our low-volume runs range from a few hundred to a few thousand units. This marked departure from the high-volume approach enables businesses to optimize their production processes and expenditures, especially when precision and customization are paramount.
In addition to the Thermoplastic polymers listed, there is also a wide range of Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) and Thermoplastic Urethanes (TPU) as well as more unusual materials such as PCU (Polycarbonate Urethane) which passes USP XXII Class VI Biological Reaction. These are generally soft, rubber compounds, used for seals, cushioning features and soft touch surfaces. These materials can be moulded in on their own as components or bonded to polymers with matching chemistry, for a chemical bond, as opposed to a mechanical bond using either overmoulding or 2-shot moulding technology.
Just about any plastic part you can think of can be injection moulded. Commonly used plastics products made by injection moulding are –
Selecting the right material for plastic injection moulding is a crucial step that requires careful consideration. To make an informed decision, it is essential to evaluate several aspects.
The injection mold structure and design directly influence various aspects of the final product, including its dimensional accuracy, surface finish,
Urethane casting can produce durable components that closely resemble injection molded parts without a significant tooling investment. This method is particularly valuable when you need robust prototypes or low-volume production.
3k or 3-shot moulding is also known as triple shot injection moulding and is similar to 2-shot but combines three different materials often to improve the strength and performance of the finished part. This process is even more complex and requires an experienced injection moulding company with specialist machines.
Different materials offer distinct properties, including strength, flexibility, temperature resistance, and durability. Selecting the appropriate material for low volume plastic injection molding is a pivotal decision. Consider the unique requirements of the project and collaborate closely with material suppliers and mold designers to make the ideal choice. This ensures that your part performs optimally, both in terms of functionality and cost-efficiency.
A further reason is design freedom and rapid prototyping that can bring new innovations to market much quicker than some other manufacturing processes.
Engineering Polymers – such as Copolyester, PBT and PET, PC, PC-ABS, Nylon and PPO. These are more expensive than commodity polymers, but provide improved thermal properties, electrical, wear and solvent resistance. Most have a higher melting point and require more expertise and knowledge for processing.

Although the first plastic injection moulding machine was invented over 150 years ago, plastic injection moulding manufacturers continue to innovate and produce ever more complex parts. This is largely due to developments in new technology, new materials and increasing demand driven by the wide range of products that are now being mass produced from plastic.
Achieving the desired surface finish is crucial, as it can impact both aesthetics and functionality. Work closely with mold designers to finesse the part’s finish, considering factors like texture, gloss, and any specific requirements for your application.
Low-volume injection molding, also called small run injection molding, is a plastic manufacturing process that typically involves producing fewer than 10,000 pieces, often ranging from 100 to 1,000 units. At its core, it involves the creation of plastic or polymer parts in quantities that are significantly smaller than those associated with high-volume production methods. This approach has gained prominence for its ability to deliver cost-effective solutions, rapid prototyping capabilities, and unparalleled flexibility in part design.
Understanding the terms related to the plastic injection moulding process and the features of your moulded parts will help you communicate effectively with plastic injection moulders, designers, or engineers involved in the process. In our demystifying blog series, we have aimed to explain common plastic injection moulding terminology.
Cost-effectiveness, versatile material selection, efficiency, speed and design flexibility are some of the benefits of using plastic injection moulding for making your parts.
These are just a few examples. The process allows for precise and complex shapes, making it a popular choice for a wide range of products. When selecting a plastic injection moulding company for your large part production, it is crucial to consider several key factors.
In the world of manufacturing, not every project calls for mass production. Sometimes, you need just a small batch of parts. This is where low-volume injection molding shines. Many niche products, limited production runs, and specialized components fall into this category. Whether you’re creating unique automotive parts, medical devices, or specialized electronic components, low-volume injection molding caters to the demand for precision and quality in smaller quantities. It’s cost-effective and efficient, making it an ideal choice for projects where quantity isn’t the primary focus.

Some plastic injection moulders offer a full end-to-end service which adds considerable value throughout the design and manufacturing process. This includes highly skilled services such as design, prototyping and toolmaking through to testing and a full validation service.
CNC Machines can be highly automated and precise. CNC machining is an alternative to injection molding for lower part volumes, especially when parts have complex geometries. Multi-axis CNC machines are often required for intricate designs.
Choosing the right manufacturing method depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of your project, cost considerations, material options, and production speed. Each alternative offers unique advantages and limitations, and the choice should align with your project’s goals and constraints.
Over moulding can be used to improve grip or reduce vibration on handheld tools or medical equipment by adding a soft touch material. Because it is a separate process, different coloured plastics can also be used to improve designs and aesthetics.
The mould design, testing and toolmaking process increases the initial costs of injection moulding, particularly for complex geometries that may need to be tested for certain defects such as warpage and surface blemishes. A skilled and experienced injection moulding company will know how to mitigate risks involved with complex parts and cooling rates and will be able to advise on material selection.
Choosing a plastic injection moulding company is a critical decision that should follow a similar approach as selecting any other crucial supplier for your business. Our series of blogs is designed to provide you with valuable insights into the factors you need to consider when choosing the right plastic injection moulding partner.
Have you ever noticed a whitening phenomenon in PVC product whitening? Some of your transparent PVC products, like shower curtains
Commodity Polymers – such as PP, PE and ABS are low cost and readily available. Many of these grades are ISO 10993 compliant for Biocompatibility.
GETTING A QUOTE WITH LK-MOULD IS FREE AND SIMPLE.
FIND MORE OF OUR SERVICES:


Plastic Molding

Rapid Prototyping

Pressure Die Casting

Parts Assembly



