
Pros and Cons of Thermoset Injection Molding - thermoset injection molding
Author:gly Date: 2024-10-15
Packaging. Overmolding contributes to the creation of ergonomic and comfortable grips on packaging machinery handles, improving operator experience and efficiency.
Consider shrinkage. Account for material shrinkage differences between the injection-molded part and overmolded material to prevent warping or dimensional inconsistencies.
What are the common applications of injection molding? What sets it apart as a manufacturing process? This article covers the key benefits of injection molding and provides insight into whether injection molding is right for your industryâs applications.
At Integrated Molding Solutions, we deliver precision plastic injection molded parts to your door. IMS provides innovative plastic solutions offering guidance and help for small and large businesses alike.
Heat staking is another permanent bonding technique. This bonding concept takes advantage of the base material being malleable plastic. The base material is heated up and the plastic reformed using a combination of heat and pressure to model the plastic around the second piece forming a hardware-free bond. One advantage is that we can use it to combine two alike or dissimilar materials. Also, it is a reasonably easy bonding process that does not require any additional parts or materials.
Enhanced functionality. Overmolding allows the integration of different materials with distinct properties, resulting in improved grip, cushioning, insulation, or sealing, enhancing the overall functionality of the product.
Quality control. Ensuring consistent bonding between different materials can be challenging, and defects like delamination or inconsistent adhesion may arise, requiring meticulous quality control measures.
Process complexity. Overmolding involves multiple steps and material transitions, increasing the complexity of the manufacturing process and potentially leading to quality control challenges.
Ensuring proper material bonding, design intricacies, and quality control are challenges in achieving consistent overmolding results.
Robotics. Overmolded grippers provide robotic systems with a balance of flexibility and rigidity, enabling secure handling of diverse objects.
Avoid sharp corners. Rounded edges and corners help prevent stress concentration and facilitate material flow during the overmolding process.
Integrated Molding Solutions is a plastic manufacturing factory in Houston, Texas. Besides plastic injection molding, some additional services we offer in the plastic manufacturing process are 3D printing, tooling, and parts assembly. Our plastic experts will take you through every step of the way through concept, design, prototype, mold manufacturing, plastic part production, parts assembly, surface finishing, a thorough inspection, and shipping. When it comes to the injection molding process, Integrated Molding Solutions is your ultimate resource for plastics manufacturing.
Venting. Integrate venting features in the design to allow air and gases to escape during injection, preventing voids and trapped air pockets.
Plastics are a growing industry that is becoming prominent in the healthcare sector. The medical industry is establishing a foothold in plastic 3D printing as a modern solution. Plastic molds help doctors to see a CT scan in 3D physically. The dental occupation often uses 3D plastic molds to custom fit parts before surgery. Research suggests that Medical grade polymers used in healthcare will positively impact growth in the medical field over the next decade.
Clamping: molds are usually fabricated into two clamshell-like pieces of metal that fit inside of a machine press. This represents the injection mold design. Molds have differing clamping pressure requirements depending on part size and geometry, material properties, and physical mold size. It is important to select the right size and tonnage (clamping pressure) of the molding machine based on these requirements.
Cooling: Water, oil, or a mixture of water and glycol, based on material temp, is distributed through the mold to cool the plastic product down. The water removes heat from the injection molded plastic while the the glycol would be mixed with the water only if the water temp will be close or slightly over water’s boiling point (212F). Hot oil is used when mold temp is even higher than that. No one wants the material to shrink or deform, so even and proper cooling is important here.
Material compatibility. Choose materials that bond well together and have similar melting temperatures to ensure a strong and reliable bond between layers.
Injection: The injection step begins when the mold, mounted to the molding machine, is closed and the plastic pellets / resin have begun melting into a liquid plastic material. Most injection machines evenly melt the plastic resin by the rotation of a screw inside of the barrel. The screw then acts as a syringe, injecting the molten plastic into the cavity. The injection molding machine monitors various parameters, including injection speed and pressure, holding pressure, clamping force, and cooling cycle time while parts are produced. To improve the part quality and reduce cycle time, process engineers and technicians adjust these parameters.
Ultraviolet (UV) bonding is another permanent bonding process. The ultraviolet bonding process carries the advantage of bonding plastics to other materials such as glass, ceramic, and metal. Bonding using ultraviolet light is a highly intense concentration of ultraviolet lighting that instantly dries or cures the adhesive. Moreover, UV bonding works in seconds to bond plastic components with other materials. A solid bond forming in moments lessens production time and often reduces rates.
Limited material options. Material compatibility is crucial in overmolding, limiting the selection of suitable combinations â and potentially restricting the ability to achieve specific material properties.
Thermoplastic over elastomer. Combining a rigid plastic such as ABS with a flexible elastomer for products requiring both durability and flexibility, like tool handles or medical devices.
Thermoplastic over metal. Coating metal parts with a protective or cushioning plastic layer, such as encasing steel components with PP, to enhance corrosion resistance and reduce noise or vibration.
What are the most common defects in the injection molding process and how do you avoid them? This article provides six essential design tips for avoid production defects while reducing the cost and lead time of your molded parts.
There are numerous products that classify as consumer goods that are manufactured by plastic injection molding. Plastic products provide cheaper alternatives while allowing custom material combinations to provide a wide range of attributes including water-resistant, heat-resistant, FDA-compliant, anti-static, and more! This material customization allows us to make many different plastic products, each with its own unique characteristics. From patio furniture that needs to be weather-resistant, to cookware and serve ware made with FDA-compliant resin, plastic injection molding can be found everywhere. Other types of consumer products are all over the beverage industry. From bottle caps and bottles, to cooling and insulation sleeves for drinkware are all made from the injection molding process.
Industrial tools. Overmolding improves ergonomics in handheld power tools, reducing operator fatigue and enhancing control during industrial use.
Ergonomic design. Overmolding enables the creation of ergonomic shapes and contours, enhancing user comfort and interaction, making products more user-friendly and intuitive to use.
Here at Integrated Molding Solutions, we go the extra mile in plastic fabrication by offering services beyond the 6 step process. After the part is ejected from the injection mold, the product or plastic part is carefully inspected and packaged for shipping. We also offer parts assembly to assemble any pieces, UV bonding to improve the component’s adhesive, and various finishing services like reducing sink marks, pad printing, or painting to provide a custom surface finish.
Find out about the manufacturing technique used to injection mold a second material over or around a part to create a new one.
Thermoplastic over thermoplastic. Using two different thermoplastic materials, such as a rigid plastic material like PC and a softer rubber-like material like TPU for improved grip or comfort.
Applying the following best practices can help ensure successful overmolding, leading to high-quality products with optimal functionality and aesthetics.
Ejection: The ejector plate pushes ejector pins which carefully push the product out of the mold cavity. We then recycle any waste for processing into recycled plastic pellets for the next injection molding project.
Overmolding involves placing an injection-molded part into a mold and injecting a second material to bond and create a single, integrated product.
When producing parts with injection molding, understanding the range of materials that are available is crucial. Find out more about those materials, their properties, and factors to consider when choosing a material for injection molded parts.
Mold Opening: The molding machine releases clamping pressure and separates the two mold halves to allow the molded part to be released.
Holding: the act of increasing injection pressure to fill the injection mold. This is where pressure is applied to the injection to fully fill the cavity.
Tool design. Design molds with appropriate gating, runner systems, and cooling channels to ensure uniform material flow and efficient part production.

Reduced assembly. Overmolding combines multiple components into a single piece, reducing the need for complex assembly processes, lowering labor costs, and minimizing the risk of assembly errors.
Want to learn how to design undercuts that donât cause damage to your parts? Check out our article, which offers tips and tricks for DFM with undercuts, examples of when you might need them, and more. Undercuts in injection-molded parts present a host of challenges to designers and manufacturers. In this article, weâll take a look at the definition of undercuts, their purpose, applications, and tips for designing parts with them.
Overmolding improves grip, durability, aesthetics, and reduces assembly steps, creating versatile and comfortable products.
Around the 1940s, the automotive industry began experimenting with plastic molding as a mechanism for automotive parts to counter the heavy weight of cars made entirely of metal. By the 1980s, manufacturers developed decorative and functional parts from plastic injection molding components. By the beginning of the 2000s, plastic became the component for structuring most cars. The most common and notable parts in the automotive industry are interior design, radio controls, air ducts, cup holders, dashboards, light housings, oil pans, mirror holders, and seatbelt buckles. There are many benefits to using molded parts, including the ability to create resin additives to achieve different product capabilities. For instance, at IMS, we use glass-filled nylon in certain car parts to provide the same performance, under high temperatures, as aluminum, but for a much cheaper cost.
Improved aesthetics. Different colors, textures, and finishes can be achieved through overmolding, enhancing the visual appeal of products and enabling branding opportunities.
Silicone over plastic. Adding a silicone layer to a plastic material such as PC for water resistance, sealing, and enhanced tactile properties.
Construction. Safety equipment such as hard hats and tool handles benefit from overmolding, providing impact resistance and improved grip for construction workers.
Design for bonding. Create proper surface features, undercuts, and interlocking structures to facilitate mechanical bonding between the injection-molded part and the overmolded material.
 Overmolding offers versatile solutions to manufacturing challenges by combining different materials to enhance product functionality, durability, ergonomics, and aesthetics. The following are several of the advantages of overmolding.Â
Did you know that most aircraft components had a dire need of replacing their metal material with plastic to reduce weight and increase durability? As a result, there has been an influx of plastic molding in the aerospace industry, from interior design paneling to functional components like compartments, buttons, tray tables, and cabin doors.
There are a wide variety of plastics used in the healthcare industry that are made from plastic injection molding. The casings for most of the monitors used in multiple industries, like healthcare, use the same method. Think all the way down to the bone of common hospital equipment and supplies, including medical devices that handle diagnostics, drug delivery services, and nutrition. IMS is expanding more into the healthcare industry with our knowledge and expertise in material selection and manufacturing injection molded parts with tight tolerances.
To get a quote for your overmolding project, start by uploading a part. You can also contact our injection molding experts with any questions or special requirements.Â
Insert molding is a systematic process of modeling thermoplastic material around an additional component. Most pliable thermoplastic resins are suitable for the insert molding process. The added piece is often a metal part. The main advantage of mold-in inserts is that generic threaded inserts are readily available in standard sizes. Generic inserts help keep costs down and avoid further customization costs. Metal inserts provide properties that plastic alone wears down over time, such as threading.
These two forms of painting apply color to the part. The painting application is ideal after molding. Painting can be any color or even metallic finishes painted over plastic. This application also helps with particular requirements such as non-static parts. In comparison, pad printing permanently places an image onto the components. Pad printing is similar in nature to a rubber stamp. An inverted image is coated with paint and laid against the part to transfer the image to the part’s surface.
Tapping and threading make for easy disassembly. Both processes produce threads on a part. “Threads” means a small threadlike ridge or groove. Tapping and threading both create threaded surfaces. The threading process makes threads on the outside surface. Like a bolt or screw, for example. Similarly, tapping creates threads inside a hole, such as a nut. Threading is performed with a die tool, while tapping uses a tapping tool. When opposite features come together, the threads interlock.
Plastic has been used over the past few decades for electronic components due to its ability to insulate electricity. From circuit boards, conduit pipes, plastic enclosures, and cases, to hardware, all of these plastic parts can be produced by injection molding. Two important capabilities are required for electronic plastic injection molding, material selection, and precision molding. Integrated Molding Solutions has the knowledge and experience, to recommend and provide the required thermoplastic resin or additives such as anti-static, flame retardant, such as ULV-0 self-extinguishing additives, to achieve your product’s specs. Additionally, we have the insert molding machines able to meet tight tolerances perfect for microchips or computer accessories.
While tooling costs can be higher, overmolding often reduces assembly and enhances product lifespan, justifying the investment.
Mechanical fasteners have the distinct advantage of offering disassembly and reassembly. Components include screws, nuts, bolts, rivets, pins, and inserts are examples of mechanical fasteners. Tapping is a process used to place threading inside a plastic injection molded hole. Advantages mechanical fasteners provide are a stronger, longer-lasting bond, durability, and disassembly. When you need to ensure the strength of the hold, mechanical fasteners are likely the correct choice.
Overmolded material placement. Position the overmolded material's injection points away from critical features and edges to avoid material entrapment or disruption.
Learn what to consider when making a choice between 3D printing and injection molding, the benefits of each manufacturing method, and more.
Integrated Molding Solutions has produced a large variety of products with plastic injection molding. We have created parts for consumer use and across multiple industries, ranging from electronics to automotive plastics, and micro components to large functional pieces. The steps taken to manufacture parts out of plastic material, from using FDA-compliant material to practicing cost-efficient shipping, are key to manufacturing in mass with high precision.
In this article, weâll take a look at common factors that influence the cost of injection molding, including equipment, labor, and materials â as well as tips for reducing manufacturing costs.
Draft angles. Incorporate draft angles to aid in easy part ejection from the mold, reducing the risk of damage during demolding.
Durability and protection. Overmolding can add a protective layer, such as a rubber coating, to shield delicate components from impact, moisture, or environmental factors, extending product lifespan.
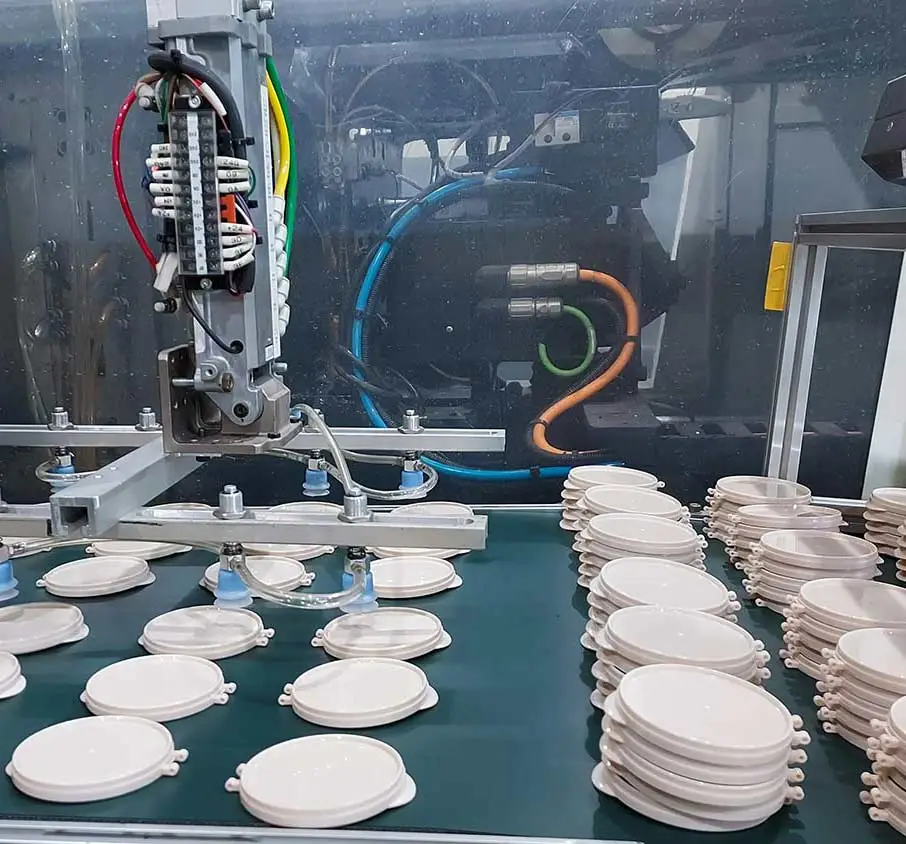

Plastic injection molding is a technique where manufacturers melt thermoplastic resin (plastic pellets), inject the molten plastic into a high-pressure mold, and then rapidly cool the mold to keep its shape. It is responsible for mass-producing millions of products across countless industries. Most molding services, like Integrated Molding Solutions, utilize this technology to produce high-quality plastic components. With 2 decades of experience, IMS offers help with any and everything plastic. From CAD design to material selection, 3d printing prototypes, manufacturing molds, injection molding, tooling services, and parts assembly, IMS is the right choice to take you from idea to production regardless of industry – especially for companies looking for molding services for the first time.
Find out about the manufacturing technique used to injection mold a second material over or around a part to create a new one.
Why is it important to design draft angles for injection molding custom parts? This article covers why draft angles are essential and how to design them better to get the most out of your injection molding designs.
Various combinations include thermoplastics, elastomers, metals, and silicone, chosen for desired properties like grip, flexibility, or sealing.
How do you optimize part design for injection molding? This complete guide to designing for injection molding provides basic and advanced design tips, including guidelines for creating snap-fits, living hinges and undercuts, and accounting for optimial surface finishes.
Injection molding was invented as an alternative to producing billiard balls from elephant tusks and saving their population. Instead of them being sculpted out of ivory tusks, John Wesley Hyatt patented the process of celluloid billiard balls in 1869 – which became the birth of plastic injection molding! He and his brother Isiah Hyatt treated nitrate cellulose with camphor and alcohol to give the balls a natural texture, like ivory or tortoiseshell, when molded along with gum shellac and other fibrous materials, into the vital piece for a game of pool. Since the invention of celluloid billiard balls, their patented injection molding process has been used to create a wide range of some of the most useful products.
Despite its advantages, overmolding presents challenges in terms of design complexity, material compatibility, production costs, quality control, and specialized tooling requirements. Learn more about the challenges in order to overcome them.Â
In overmolding, a variety of materials can be used to achieve specific properties and functions. Several common combinations include:
Medical equipment. Overmolding is employed in medical device housings, enhancing durability and ergonomic design for instruments like handheld scanners and diagnostic tools.
Electroplating or electro-deposition is a process whereby a metal material coats the surface of a part. In the electroplating process, a permanent bond connects the metal to the surface of another piece. The process involves an electrolyte or plating bath charged with electricity. The electricity-charged bath deposits small particles of the metal over the part’s surface. Therefore, this process effectively coats the plastic piece in a completely shiny, smooth metal finish.
Electronics. Overmolding ensures durability and strain relief for cable connectors, safeguarding cable connections in challenging environmental conditions.
In injection molding, âovermoldingâ refers to a process where multiple materials are used to create a cohesive, often multi-textured product with improved qualities and versatility. Hereâs a guide to using the technique, including how it works, its common industrial uses, and more.
Complex design and engineering. Overmolding requires careful design considerations and engineering expertise to ensure proper material compatibility, bonding, and mold design, which can increase development time and costs.
Costly tooling and equipment. The need for specialized molds and injection molding equipment tailored to overmolding can lead to higher initial investment and tooling costs compared to traditional molding processes.
Electronics are still a leading sector in the use of plastic resin parts. Plastics do not conduct electricity. Electronics often need plastics to insulate the electricity running through them. Consequently, a plastic part can make the perfect insulator for electronics and electrical devices. Plastics also have a lower conductivity for heat. Meaning, that plastics do not transfer heat well due to their insulating properties. This particular property works to the advantage of the plastics industry when it wishes to shield heat from other more delicate parts or the user. You may also treat plastics with special flame retardant finishing applications to further support their fire-resistant properties.
Want to learn more about die casting? In this article, weâll take a look at the process, its history and current uses, advantages, design guidelines, and more.
Want to learn more about exactly how an injection molding machine functions, as well as its individual parts? This article puts injection molding machines under the microscope, with detailed descriptions of their components and an in-depth guide to the injection molding process.
What is Delrin and why is it unique among the many manufacturing materials available? Delrin, or POM-H (homopolymer acetal), is used in CNC machining, 3D printing and injection molding to create durable, precise components. This article explores Delrinâs properties and how to get the most out of the material.
Overmolding works by first placing the injection-molded part into a mold. Next, a second material is injected over or around the part. The two materials are then bonded together during the curing process.
Proper wall thickness. Maintain consistent and appropriate wall thickness to ensure even material flow and prevent defects like sink marks or voids.
Aerospace. Within aircraft interiors, overmolding enhances passenger comfort and cockpit functionality, seen in armrests, seat cushions, and control grips.
Overmolding is a manufacturing process that is often used in injection molding, in which a part is encased or covered with a second material â typically a rubber or plastic â to create a single, integrated product. It enhances product durability, grip, aesthetics, and functionality.
The automotive industry is controlling fuel efficiency by switching to lightweight plastics. Using plastics for many auto parts reduces the vehicle’s overall weight and increases fuel efficiency. With the need for better fuel economy solutions, the automotive business has turned to plastics manufacturing for many automotive components. Additionally, government regulations recently are pressing the automotive industry to move from iron and steel to plastics. This push from the government is shifting the automotive industry towards higher-grade plastics in place of metals. The recent drive for a plastic manufacturing process in the automotive segment allows us to anticipate that injection molded plastics will increase rapidly under these new regulations.
Level up your injection molding knowledge and find practical tips about selecting materials, working with draft angles, and reducing costs.
GETTING A QUOTE WITH LK-MOULD IS FREE AND SIMPLE.
FIND MORE OF OUR SERVICES:


Plastic Molding

Rapid Prototyping

Pressure Die Casting

Parts Assembly



