
Polylactic Acid (PLA) at Aline Components - pla injection
Author:gly Date: 2024-10-15
Injecting plastic into a mold that already has an insert in place is known as insert molding. This insert aids in the part’s shaping. The pre-placed insert inside the mold is the only distinction between insert moulding and regular injection moulding. This insert may be constructed from metal or a variety of plastic materials.
Inexpensive, higher impact resistance in some grades, PP homopolymer can be brittle in cold. Wear resistant, flexible with high elongation. Resistant to acids and bases. Density less than water (floats)
Modulus is provided on virtually every data sheet. Most often this is provided as tensile modulus or flexural modulus. The modulus relates stress to strain and can be thought of as a measure of stiffness. In most cases the modulus is calculated in the linear region of the stress-strain curve. Linearity often is lost at very low strains. Figure 1 shows a magnified view of the early portion of a stress-strain curve for a highly-glass-fiber-reinforced nylon 6/6. While the modulus of this material at room temperature is given as 10600 MPa (1,537,000 psi), the graph shows that the stress-strain plot departs from linearity at approximately 0.4%. Beyond this point each incremental increase in stress produces a progressively larger corresponding strain. Figure 2 shows that while the slope of the modulus line reflects the value provided on the data sheet, the effective slope of the line connecting the origin to the yield point has a slope that is only 40% of this reported value. Therefore, when using the modulus as a selection property it is important to understand the position of the application stress on the stress-strain curve. As application stresses approach the yield point the expected lifetime of the product declines. Table 2 shows the maximum operating stress for a polycarbonate material as a function of time at two different temperatures. At very short times, less than an hour, the stress limit is nearly the same as the yield stress for the given temperature. As the time frame of the application increases under load, the maximum allowable working stress declines.
A typical plastic injection molding procedure is overmolding. In overmolding, a product is made from two or more materials. For instance, overmolding enables the creation of a plastic toothbrush with a plush handle. The exterior layer is referred to as the overmold material, while the center, typically the tougher portion is referred to as the substrate.
Another is to overmold material of a different color or finish to an item in order to alter or improve its look or “cosmetics.” Anything from toothbrushes to medical equipment(like medical plastic injection molding producer), hand tools, and assembly gaskets and seals can be made with overmolded materials.
We have a team of experts at SeaSkyMedical who can assist you with including overmolding in both your design and manufacturing phases with the help of our overmolding factories, so be sure to contact us. If overmolding is too expensive for you, we are pleased to assist you to find an alternative route that will produce comparable results.
Tough, impact- and chemical-resistant, high shrink, low dimensional stability, inexpensive, density less than water (floats)
However, one drawback is that it is readily scratched, making it very sensitive to use. Furthermore, because it is made of oil and emits hot plastic vapors during production, it has the potential to be extremely harmful to the environment.
All polymers have a long-term sensitivity to oxygen and this sensitivity increases at higher temperatures. Degradation associated with aging is captured by a property called the “relative thermal index,” or RTI. This value comes from a test mandated and administered by Underwriters Laboratories. It is currently the best gauge for measuring the long-term effects of aging on the mechanical and electrical properties of polymers. RTI testing begins by measuring key baseline properties such as tensile strength, notched Izod impact resistance, and arc resistance. Test specimens are then aged at multiple temperatures and the baseline properties are monitored until they decline to 50% of the original values. The time required to reach 50% performance is called the “time to failure.” If three or four aging temperatures are used and the logarithm of the time to failure is plotted as a function of reciprocal temperature, the data points can be fitted to a straight line. This line is then extrapolated to a standard time (normally, about eight years) and the temperature predicted to cause failure at the standard time is the relative thermal index. For most thermoplastics the RTI values are lower than DTUL and Vicat softening values. This is the case for the glass-filled PBT in our Appendix A sample data sheet where the DTUL and Vicat values are all above 200°C (392°F) while the RTI values are 140°C (284°F). However, it is possible for soft, flexible materials with good oxidative stability, such as PTFE, to have RTI values that are higher than their DTUL numbers. RTI values can be used to predict long-term performance where aging is the primary concern.
Acrylic is one of the materials listed for injection molding that comes in a thin sheet and is frequently used as an alternative to glass. PMMA makes use of a wide variety of goods, including windows, eyeglass lenses, and car taillights. The benefits of acrylic include its high sheen, strong abrasion resistance, and ability to withstand weathering. However, it only has a limited heat resistance and is brittle under pressure, which is its drawback.
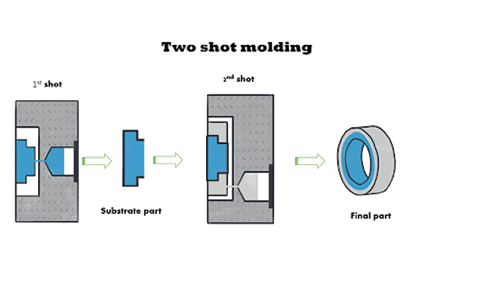
Two or more components are molded on top of one another during the multi-step injection molding process known as overmolding. Due to the fact that overmolding is a two-step procedure, it is occasionally referred to as two-shot molding. A base component often referred to as a substrate, is first molded and given time to cure. Substrates for overmolding are frequently composed of plastic. To produce a single, solid component, a second layer is then directly formed on top of the first.
Slide bearings, gears and cams; coffee makers and toasters; hair dryer nozzles; vacuum cleaners; handles and knobs for electrical cookers.
Comparisons of materials based on melt flow rate are only valid if they are made within a particular polymer family. In addition, some materials employ multiple conditions for testing. For example, ABS can be tested in different conditions defined by the temperature and the load that is placed on the material. These test conditions are shown in Table 4 along with the typical differences in the results associated with each condition. When comparing two grades of materials it is important to note the test parameters and adjust accordingly.
Tough Black (Loctite Henkel 3843) and Ceramic-Filled (BASF 3280) are two new advanced photopolymer materials now available for 3D printing.
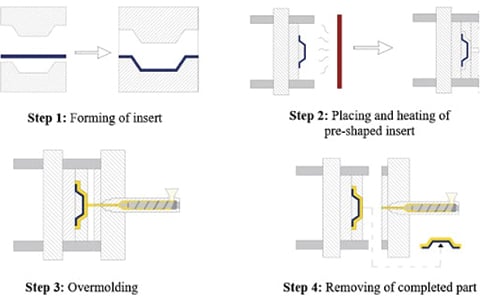
If two different pieces are bonded together in an injection mold, there is a possibility of delamination. When the ideal temperature range fluctuates, delamination will happen. When the materials cannot be properly bonded together with the heat available, mechanical interlocks are required.
The drawbacks are that it can be weakened by UV and lose 70% of its power when exposed to sunlight. Additionally, it may be combustible because of the chemical it contains.
This guide to thermoplastics and injection molding material selection is aimed at an engineer who plans to quantitatively analyze a part, determine loads, stresses, strains, and environments and make an optimal material decision based on the analysis. If life safety is involved, or reliably or efficacy are absolutely required, every part should be engineered and materials selected accordingly. If you look through this paper and see the many factors involved and how environment and application influences material selection, you can understand why an engineer will be very reluctant to recommend a specific material for someone else’s part.
The standard material data sheet consists almost entirely of performance characteristics measured at room temperature. In addition, the performance characteristics are associated with catastrophic events that are not considered to be an acceptable outcome for engineered plastic products. Tensile strength at yield and elongation at break represent the standard metrics of material performance, but yield and break are not the desired responses of plastic parts when they are placed under load.
Melt flow rate is a property that appears on most property data sheets. It is an attempt to capture an important aspect of material behavior with a single number. Melt flow rate is often used by processors as a gauge of how a material will flow during molding. The significance of the melt flow rate value is its relationship to the average molecular weight of the polymer. Lower melt flow rate values are associated with materials of higher average molecular weight. Higher molecular weight, in turn, provides for improved properties, especially in the areas of impact resistance, creep and fatigue performance, and barrier properties.
Overmolding can be a powerful tool in product design, but it necessitates extreme care and consideration when the design is being developed. Overmolding can increase expenses during the design and development stage, but it can also save long-term production costs and increase the value of the final product.
Determining the appropriate material for your application involves synthesizing information from a variety of incomplete sources. The data-sheet is the primary source of information, and you should learn to extract as much information as possible from this source. Appendix A shows a data sheet for 30% glass fiber-reinforced PBT polyester. This is a good example of a reasonably detailed data sheet.
High-temperature tolerance, dimensionally stable, high toughness. Resistance to radiation sterilization, as well as alkalis and weak acids
On the other hand, overmolding refers to the process of creating a single part or product from more than one material. Insert molding is shown in the portion of the figure above where the substrate is injected over the bolt. Overmolding, a technique for enhancing grip for parts, is the term for the additional rubber layer that is placed around the nail.
The upper-temperature limit for filled or unfilled amorphous polymers can also be found by looking at HDT or DTUL. For example, for unfilled polycarbonate the HDT values range between 130–140°C depending upon the grade. Vicat softening points, where provided, are a few degrees higher. Amorphous polymers do not show a significant crystalline structure when they solidify, therefore they do not have a melting point. However, they do exhibit something called “glass transition.” From a practical standpoint, this is the temperature at which amorphous polymers lose their load-bearing properties.
Elastomer, often known as thermoplastic rubber, is another substance used in injection molding. Rubber and plastic parts are mixed together in it. used in other applications as a home appliances and for automotive parts like wire and cable insulation. The benefits include the flexibility to stretch and recover to its original shape.
The customer’s desired colors can be used to create custom or pre-set automotive trims. In order to be molded with additional materials, such as steel, chromium, or any type of metal plating, these overmolded trims can also go through a different procedure known as insert molding.
Wide variety. High strength and temperature tolerance when reinforced. Chemically resistant except to strong bases or acids
Making thermoplastics is frequently accomplished through the use of injection molding. While there are several popular plastics that can be used for clean room injection molding, material selection can be challenging. There are many distinct types of plastic injection molding materials, each with a specific function.
The perks include its superb quality and practically intolerable bullet resistance. It also guards against discoloration, however prolonged UV light exposure might cause it to turn yellow. Additionally, it can be scratch-sensitive.
The benefit is that polyurethane has exceptional toughness and flexibility, is resistant to impacts like tearing, and is resistant to lubricants like grease and oil. Due to its low reactivity to tearing over time, it has good dimensional stability. However, one drawback is that, compared to other options, it is not cost-effective. It has a limited shelf life, too.
Proto Labs, Inc. 5540 Pioneer Creek Dr. Maple Plain, MN 55359 United States P: 877-479-3680 F: 763-479-2679 E: [email protected]
Plastic overmolding is the process of producing two different types of plastic parts in one (or two different colors of plastic parts in one solid part) using a standard single-nozzle injection molding machine. The over-molded process entails moving the first part (the substrate part) or melting inserts (insert molding) to the subsequent mold (the over-mold) and molding to obtain the final part.
Good electrical properties for power components and works well for automotive applications. Moderate to high strength depending on glass fill. Unfilled grades are tough and flexible. Good resistance to fuels, oils, fats, and many solvents. Doesn’t absorb flavors. Low creep.
The process of overmolding is frequently employed to create plastic components with rubber handles. For instance, in the two-shot method of overmolding a toothbrush, a base layer for the plastic handle and a top layer of rubber are formed (to make the toothbrush less slippery to hold).
Polypropylene, also known as polypropene, is the final material we will examine for injection molding. A thermoplastic polymer with a wide range of uses, polypropene is expected to have the highest revenue share in 2020, at 34.2 percent. Due to the fact that it doesn’t combine chemicals with food goods, it is most frequently used in the food storage and packing business. This material’s excellent impact strength and good moisture resistance are further advantages.
Strong, extremely impact resistant, low shrink, good dimensional stability and heat resistance, accepts high cosmetic finishes well
A consultant usually won’t make a material recommendation without understanding the complete application requirements for the part, and without running a design analysis on the 3D model of the part. Sometimes, it’s not cost-effective to fully engineer the part to come up with a material selection. If you want to short-circuit the materials engineering and take an educated chance on material selection, here are a few rules of thumb you can use:
Show knit lines and can have sink and voids in thick areas. You might be able to reduce sink by switching to an ABS/PC-blend.
The primary machining components for these materials are typically composed of tool steel, which can be used for cutting, bending, drawing, punching, and other sorts of fabricating processes. But before the steel can be used, it must be handled safely and ergonomically by the end-user; this is where overmolding comes in.
Overmolding is completed in one cycle of operation. As a result of the lack of two- or multi-part assembly, the procedure is accelerated. They can lower their manufacturing costs and accelerate the entire process because overmolding eliminates the post-assembly stage.
Low-density polyethylene is a lot softer and more flexible than high-density polyethylene. Bottles, plastic bags, and wraps, as well as playground slides, are all made with low-density polyethylene using the injection molding process. The resistance to chemicals and moisture of this material is advantageous. Additionally, it is affordable and of a high enough quality to be used in food, making it safe.
Properties other than thermal and mechanical can be important in specific applications. These include electrical properties such as dielectric constant and strength, surface and volume resistivity, and coefficient of thermal expansion. Standard measurements of the coefficient of thermal expansion are made between -30°C and +30°C. However, some suppliers will provide values across multiple temperature ranges such as those represented in Table 5. When this more complete picture is available it shows that these types of properties are also dependent upon temperature and the values tend to increase with increasing temperature.
Seasky Medical serves you with medical injection molding solutions from design to tooling to material selection and manufacturing. Contact our specialized team and solve your problem now.
Can be brittle. PC is a good alternative. Draft always required, sometimes twice as much as other materials. Poor chemical resistance.
Material selection can be a guessing game. First, there is a general gap in understanding the fundamental relationship between the internal structure of the material and its properties. Second, accurately defining application requirements is usually given insufficient time and attention. Finally, even when these first two hurdles are overcome it can be hard to find accurate property data for materials.
For polycarbonate this value, when measured by dynamic mechanical methods, is approximately 153°C, just a few degrees above the Vicat softening point and 10–20°C above the DTUL, depending upon the specimen geometry and how the DTUL is measured. Vicat softening temperatures and DTUL values should never be used as long-term performance characteristics. However, they can be used to gauge short-term heat resistance when short-term is defined in minutes. Any application environment that involves excursions to temperatures above these properties will eliminate that particular material from consideration regardless of any other attributes it may possess.
TPU offers a wide range of characteristics, including flexibility, transparency, and resistance. Its soft and hard portions are its characteristics. This kind of plastic is primarily used to make footwear, keyboard covers, and phone cases.
Utilizing a 2K injection molding machine, 2K injection molding is the process of producing two or three different materials (colors) as one solid part. Although the molding process is complex, it is quick, effective, and of high quality, and 2K molding units are less expensive than plastic overmolding.
Almost any type of consumer or industrial object can be produced using the overmolding technique, including grips, handles, knobs, electronic components, moldings, bottle caps, and automotive parts. Customers are free to create their own overmolded goods as long as the resins and raw materials they employ are compatible.
Glass-filled PBT resins are prone to warp, and have poor resistance to acids, bases, and hydrocarbons. Thin parts hard to fill with PBT. Nylons are good alternatives.
Get machined parts anodized and chromate plated with our quick-turn finishing option. Eligible materials include aluminum 6061/6082 and 7075.
Possible sensitivities in thick sections of parts could cause voids, bubbles, and sink. Poor chemical resistance. An ABS/PC blend is a good alternative for opaque parts with these issues Acrylic is another option for parts with thick geometries.
POM, often known as acetal, is a robust, hard plastic injection molding substance that is made of polyoxymethylene. Automotive parts can be made using acetal. Acetal is also used in the manufacture of zippers, fan wheels, door handles, lock mechanisms, and insulin pens. The benefits include its high gloss finish and resistance to organic solvents and chemicals, with the exception of phenols.
Long-term performance when a material is under constant stress involves a property called “creep resistance;” if the stress is periodic then fatigue resistance becomes the dominant consideration. The relationship between stress, time, and temperature is complicated and frequently the data needed to make good decisions about long-term behavior of a material under load are not available. Here again the data sheet can provide an upper limit. The upper limit for ductile materials is the yield strength of the material and for brittle materials it is the stress at break. Both values define the point at which the material fails catastrophically. Any environment that involves stresses and strains higher than these values eliminates the material from even short-term consideration. Beyond this simple filter, you will next need to look at long-term temperature effects.
In comparison to plastic overmolding and 2K injection moulding, 2K injection moulding has higher quality and greater production efficiency; however, because the 2K injection moulding machine is more expensive, over-molding is occasionally used to replace it. However, plastic overmolding can be produced using any standard injection moulding machine, making it more cost-effective for low-volume, two-color moulding.
Because of this, distribution periods for the finished product to various manufacturers and suppliers at different levels for OEM or aftermarket usage are shortened. The injection molding business can enhance production capacity with decreased manufacturing expenses.
Having said that, overmolding has also been widely utilized in this business. Overmolding is a process used to make a variety of medical products, including housing for equipment and surgical instruments, to produce a final portion that facilitates use. Syringes, patient monitors, lab consumables, needles, catheters, dilators, soft-touch buttons, and many more are a few examples.
Seasky Medical serves you with medical injection molding solutions from design to tooling to material selection and manufacturing. Contact our specialized team and solve your problem now.
Low density also has the drawback of being potentially flammable and having weak temperature capability, making it risky near a fire. Additionally, it can be challenging to connect and has weak weather resilience.
Overmolding is another name for co-molding. It speaks of the joining of two plastic materials, typically a hard material like ABS and a soft material like TPE. Nevertheless, depending on the melting temperature, two identically hard materials might be able to join together.
As an injection molding material, nylon has various benefits. One is that it is durable and elastic in nature due to its superior abrasion resistance. On the other hand, the material’s tendency to melt easily is a drawback. This makes using the material in its liquid condition difficult. Additionally, it directly or indirectly collects water from the air’s moisture.
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene is known as ABS. This type of thermoplastic injection molding material is commonly found in pipes, car body pieces, and keyboards. In addition to its beneficial qualities, ABS also offers a number of advantages. For instance, the material’s excellent impact resistance makes it difficult to break because it is strong yet lightweight. Additionally, it is heat- and temperature-resistant.
Evaluating impact performance from typical data sheet values is challenging because the industry employs many different methods for testing impact resistance and reporting the results. The most common test method for evaluating impact resistance is the notched Izod test. The test employs a specimen with a sharp notch machined into the part and a swinging pendulum is used to impart the energy needed to produce failure.
In many hardware tools, overmolding is perfectly illustrated. These might include blades, pocket knives, pliers, wrenches, hammers, tape measures, and other similar tools.
Predicting long-term elevated temperature performance requires access to multiple data points. As the temperatures increase or as the desired lifetime of the product increases, the allowable stress level at which the material can be used decreases according to a function that is dependent upon the thermal and mechanical properties of the specific material. Correlations between short-term and long-term performance have shown that the long-term working stress levels for a thermoplastic will typically be between 20–40% of the short-term strength at yield or at break. Unfilled materials tend to fall in the lower end of this range while highly filled compounds tend to fall into the upper end of this range. Safety factors for a given product will reduce these values and if the temperature of the application environment approaches the DTUL values it is possible for the sustainable working stress to be only 3–5% of the value provided on the data sheet. Some data sheets will give tensile strength and modulus values at multiple temperatures. If available, these data can eliminate a lot of guesswork. Table 1 gives an example of tensile strength values provided at multiple temperatures for a glass fiber-reinforced nylon 6/6.
If you’re going to mold parts, you might try having a couple test parts in the target material made by our CNC machining service before committing to a mold. Molds are designed to match the shrink rate of a particular resin, so it may not be possible to run multiple resins in the same mold without risk to part size, tolerances, and/or dimensions.
Our helpful design aid demonstrates part features that are too thin or too thick, bad bosses, right and wrong ribs, and other considerations to be mindful of while designing parts for injection molding.
Maximum short-term use temperature is possibly the most important data sheet parameter. Traditionally, this is the deflection temperature under load (DTUL), also called the heat deflection temperature (HDT). Another related parameter is the Vicat softening temperature. Because DTUL measures mechanical deflection and the Vicat point is closer to the actual melting or softening point of the polymer, the Vicat number will typically be higher. For a material such as the glass reinforced PBT of Appendix A, which is a semi-crystalline material, all of these values will be very close to the crystalline melting point of the polymer, 223°C (435°F). Any application that involves even momentary excursions above this temperature will eliminate this polymer from consideration.
Thick sections could result in voids, bubbles or sink. Organic solvents and hydrocarbons can also attack PPSU. Colorant cannot be added to Protolabs-supplied PPSU resins
We must comprehend the two elements of the process in order to have a better understanding of how it functions. Each overmolding job is divided into two components. The substrate is the first step in the process, while the overmold is the second.
More detailed information can sometimes be obtained from design manuals and application notes published by individual material suppliers and can fill in the gaps in the data sheet. Supplemental information is usually more available for higher performance engineering and specialty materials than it is for commodity materials. If you really want to understand a material you need to be prepared to do a little detective work.
Overmolding necessitates the assemblage of several components. Utilizing all of the advantages of the materials used increases the part’s flexibility. Additionally, producers can increase flexibility by using the overmolding design guide.
Precision and product safety are important factors in the medical sector. When employing various kinds of surgical tools, professionals like doctors, surgeons, nurses, and medical equipment parts manufacturers and medical device contract manufacturing companies should also be able to rely on safe plastic materials. Additionally, in order to avoid infection, this equipment should be sterile and simple to clean.
High-performance material, very expensive. Ultem (outlined below) is a slightly less-costly option, and PPSU is worth considering if price is a concern.
A machine part or component made by fusing two or more materials together is the end product of the overmolding process. Either the same materials or alternative materials can be used. There are essentially no limits to the material combinations.
Gears, pumps and pump impellers, conveyor links, soap dispensers, fan and blower blades, automotive switches, electrical switch components, buttons, and knobs.
High-temperature, high-performance, flame retardant; excellent strength and dimensional stability, good chemical resistance
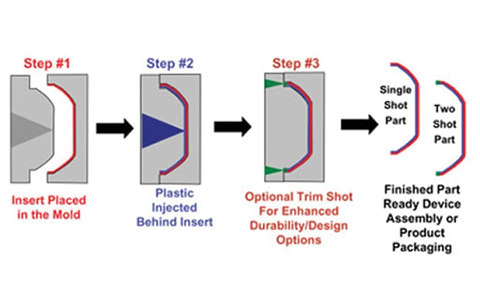
However, many of Protolabs’ customers who design parts are not engineers, and many applications of Protolabs manufactured parts are quite benign and are expected to stay well within the performance envelope of common plastics. If your application lives at room temperature, it doesn’t have appreciable loads, and you’re willing to make a few parts and whack them with a hammer to see if they’re strong enough for your use, look for the simplified suggestions for selecting materials at the bottom, called “Don’t Make Me Do the Math.”
Some material properties are strain-rate dependent. The rate at which the material is loaded will have an influence on the modulus as well as the yield stress as is shown in Figure 3. Higher strain rates produce greater values for modulus and yield stress. While it is desirable for all suppliers of a given type of material to use the same strain rates when testing, this is not always the case and there can be apparent differences in data sheet properties caused by this lack of harmonization.
Cosmetic parts, handheld devices, housings, and moldings for electrical tools, remote controls, computers, telephone components
Good optical properties, high gloss, scratch resistant. Low shrink, Less sink in geometries with thin and thick sections.
High-temperature, high-performance, flame retardant, excellent strength and dimensional stability, good chemical resistance.
Falling dart tests such as the Gardner test or the instrumented falling dart impact test can provide additional data points. These tests use specimens where no stress concentration is machined into the part and give a more accurate reflection of the performance that can be expected from a well-designed part.
Impact properties are also influenced by temperature. Lower temperatures are more likely to produce brittle behavior in a material and the transition from ductile to brittle performance can be very sudden. It can be difficult to find a complete picture of this type of behavior because material suppliers are reluctant to report on unfavorable performance characteristics. However, a search can yield valuable results even if these results are not available for all materials. Figure 5 shows the notched Izod impact behavior for different grades of polycarbonate as a function of temperature. These results illustrate the rapid change from ductile to brittle behavior that typically occurs as a function of declining temperature. This graph also shows that the transition from ductile to brittle performance is related to the molecular weight of the polymer. The lower melt flow rate values are associated with grades having higher average molecular weights. This property has a significant influence on the temperature at which the impact performance changes.
An existing molded object can have a second layer of resin added to it using the tpu injection moulding technique known as overmolding to provide a combination of properties that no one material can. One of the most popular uses is to place a TPE (thermoplastic elastomer) layer of soft, useful, and hand-friendly rubber-like material over a hard substrate.
Due to its diverse nature, nylon, also known as polymer fabric, is one of the most adaptable injection molding materials. Along with fishnet and insulators, it is utilized in fish tires, automotive tires, and many types of clothing.
Plastic must always be food-safe when used to make things like cookware, food containers, and kitchen utensils. Given this, it should come as no surprise that overmolding should be a crucial process used in the production of cookware parts and components.
As was previously noted, one benefit of overmolding is that it enhances grip, use, and cleanliness in numerous products. In addition to these, overmolding uses components to increase a product’s chemical resistance, vibration dampening, sound insulation, and many other properties.
Overmolding is used in cookware for a variety of purposes, such as spatula handles, pot covers, strove trimmings, knives, cutting boards, and more. These products use high-grade polymers that won’t compromise the flavor or freshness of food, boosting consumer safety.
Tough, stiff, hard, and strong. Good lubricity and resistance to hydrocarbons and organic solvents. Good elasticity, slippery. Low creep. Great fatigue properties.
Modulus changes with temperature. A data sheet that lists modulus values for multiple temperatures such as those shown in Table 1 will create a more complete picture of a material’s behavior. However, it is rare to find data for more than four temperatures and these can span a range of 150–200°C, leaving a great deal of uncertainty about the behavior of the material between these points or outside of the range defined by these points. Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) allows for a continuous measurement of modulus over a wide temperature range. Figure 4 shows modulus versus temperature curves for polycarbonate, an amorphous polymer, and nylon 6, a semi-crystalline polymer.
The substrate and the overmold material are frequently physically interlocked as well as chemically linked while making an over-molded component. This makes it more likely that the components will be assembled as a single unit. Many medical molding companies use overmolding for their benefit.
Plastics are generally considered to be excellent electrical insulators unless a compound is made specifically to dissipate static or be somewhat conductive through the addition of ingredients such as carbon or stainless steel. Therefore, values for resistivity are very high for most materials, between 10^10 and 10^16 ohms or ohm-cm for surface and volume resistivity, respectively. Sustained electrical stress can result in the dielectric breakdown of a material over time. This behavior will depend upon the magnitude of the voltage being applied and is captured most effectively by properties that may be part of the standard data sheet but may be more readily found in the Underwriters Laboratories database as part of their Yellow Card system. This method applies numerical values to properties such as high amperage ignition, arc track resistance, and continuous tracking index with the lowest values for each metric indicating superior performance and higher values associated with lower levels of performance.
Transparent polycarbonate is a robust, durable injection molding material used in engineering. Bulletproof glass, safety hamlets, compact discs, and other electrical and telecommunication technology all contain PC.
Overmolding has the benefit of enabling the design and production of unique plastic components for virtually any business. Overmolded items with high dimensional quality can be produced by manufacturers using a plastic-plastic or metal-plastic combination.
The aging process follows an empirical rule that relates degradation to temperature. The rate of degradation doubles with each 10°C increase in temperature. This is an exponential relationship so a change of 20°C will increase the degradation rate by a factor of 2^2 or 4 while an increase of 30°C increases the rate by a factor of 2^3 or 8. Since RTI is indexed to a time frame of approximately eight years, you can estimate that a material could survive for four years at a temperature 10°C above the RTI, two years at a point 20°C above the RTI, and one year at a point 30°C above the RTI. Safety factors should be built into this calculation since studies show that the actual acceleration factor, while nominally 2, can vary from as low as 1.8 to as high as 2.5.
If a chemical is present in the application environment that is capable of inducing a phenomenon called “stress cracking,” the maximum operating stress declines. Table 3 shows the maximum working stress for the same polycarbonate profiled in Table 2 where the constant stress is coupled with the presence of a fluid that acts as a stress crack agent. It shows that the mechanical capability if the declines compared with the properties when this chemical is absent. Failure of a plastic under the combined influence of stress and a chemical agent is called environmental stress cracking (ESC) and it is the most common cause of field failure in plastic parts.
Overloading does not require adhesives since overmolding allows diverse parts to fuse together naturally. As a result, the products’ durability improves. The cost of production has decreased overall as well.
The production procedure involving overmolding involves two processes, lengthening the part cycle time. When you need to mold multiple parts in a single process, the cost of production tends to rise. Additionally, because overmolding is a two-step operation, it takes more tools than a single molding.
The drawbacks of HDPE include its high flammability and lack of biodegradability, which makes it difficult to dispose of. High-density polyethylene also has poor weathering and cannot be assembled.
More than 85,000 commercial options for plastic materials are listed in materials databases, and the real number is probably over 90,000. This extensive set of options can be sorted into approximately 45 polymer families or blends, and these 45 families can be further divided into two broad categories: thermosets and thermoplastics. While thermosets were the first commercial polymers, their use has diminished to the point where they constitute only about 15% of all the material processed in a given year. Therefore, this paper focuses on thermoplastics.
Thick sections in part geometry can void or show sink marks. Shrink and warp possible. If the part has living hinges that require higher stiffness, K-Resin is a good alternative.
The pieces that are located in various regions of the automobiles, such as the door edge, side body, fender, bumper, wheel, and other areas in the interior, are referred to as car trims or car moldings. Car trims have certain practical advantages, particularly in lowering the weight of the vehicle, despite the fact that they are frequently fitted for their visual appeal.
High-density polyethylene is a thermoplastic that is used in injection molding and is mostly used to make plastic bottles, shampoo bottles, toys, and recycling bins, and flower pots. The key benefit of choosing HDPE is that it is both reasonably priced and made of rigid, highly durable material.
The minimal radius in the Izod notch often exaggerates differences in ductility because of differences in notch sensitivity among materials. For example, polycarbonate and amorphous PET polyester both possess good practical toughness. PET polyester is more notch-sensitive that polycarbonate. Consequently, the notched Izod impact values for polycarbonate at room temperature may be much higher than those for some grades of PET polyester, giving the impression that polycarbonate is a much tougher material. A more complete picture of impact performance can be obtained if impact results can be obtained from different types of impact tests.
Our digital factories create prototypes and low-volume parts fast, while our manufacturing network, offers advanced capabilities and volume pricing.
Because it doesn’t contain recyclable, non-toxic plastics, it is also less harmful to the environment. Additionally, obtaining this material might be rather expensive. The material can withstand high temperatures, although doing so could cause it to lose its rubbery quality.
Medical instrument components, sterilization trays, automotive fuses, interior aircraft parts, hot water fittings, sockets, and connectors.
The substrate serves as your starting point. Any of a huge range of materials could be used. Your overmold is the auxiliary substance. You want to “mold over” the substrate with this substance. There may be two or more overmolds present in some circumstances. The amount of overmolds is entirely dependent on the final product that is sought and the manufacturer’s creativity.
Including additional high-quality materials improves a product’s performance greatly. Overmolded items have two material advantages over standard products utilized in industries. Because of this, overmolded items perform better.
Thin-walled features, combs, spools, gears and bearings, screws, structural parts (with glass), pump parts, under-hood components, cameras.
It should come as no surprise that many common home objects, including toothbrushes, kitchen utensils, portable electric fans, mirrors, pens, multi-port chargers, shampoo bottles, reusable food containers, and the like, are created from overmolding.
These two materials represent behavior typical of their respective structures. Both possess a glass transition that represents the onset of molecular motion in the amorphous regions of the structure. In the amorphous polycarbonate this results in the complete loss of all useful mechanical properties over a relatively narrow temperature range. However, in the nylon the decline in modulus, while significant, is not catastrophic and about 20% of the room temperature performance remains. This is a measure of the contribution of the crystal structure in the polymer. All amorphous polymers exhibit temperature-dependent behavior that is similar to that of polycarbonate, and all semi-crystalline materials display a property-temperature profile that is similar to that of nylon. The essential differences are in the exact transition temperatures for each polymer.
GETTING A QUOTE WITH LK-MOULD IS FREE AND SIMPLE.
FIND MORE OF OUR SERVICES:


Plastic Molding

Rapid Prototyping

Pressure Die Casting

Parts Assembly



