
Low-Volume Injection Molding - low volume injection molding
Author:gly Date: 2024-10-15
Less expensive tooling not only saves on the initial production costs but also lowers the cost of design changes and modifications.
These disadvantages are mitigated by speed, the accuracy of detail, and affordability. In this process, a laser beam traces cross-sections on a photocurable liquid resin layer after layer. A platform beneath can move upward or downward inside a vat filled with photopolymer liquid resin by accurately controlling a horizontal elevator located underneath the vat. Cross-sections of 3D objects are formed one layer at a time through ultraviolet light exposure from below on each liquid resin cross-sectional layer as the elevator moves downward step by step while creating parts from up until the final product is complete.
Every project has an ideal process. If you’ve been considering RIM for anything beyond initial prototyping for your next custom plastic fabrication and plastic manufacturing project, we’d recommend that you look at the advantages of thermoforming before you make up your mind.
Rapid prototyping enables manufacturers to produce multiple variations of a part quickly and easily, at costs effective enough that almost any conceivable design can be economically feasible. With rapid prototyping, you have the ability to experiment with designs until you have the ideal solution before committing to costly production tooling, which is not financially feasible if it means being stuck with some less-than-perfect tooling or trying out a new manufacturing process on your high volume products.You’d even need an accurate drawing for a rapid prototype. You can turn a rendering or CAD drawing into a model, even if it is missing dimensions and doesn’t have all the features right yet.Rapid prototyping has been used to create low-volume models from time to time because of its cost-effectiveness but is now being used as a way to cut costs on high-volume parts as well. The process allows designers and engineers to produce a single part that can be directly translated into a production piece using CNC machines and existing tooling processes. It is used frequently for automotive lighting prototype.
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Selective Laser Sintering, also known as laser sintering, selective heat bonding, or direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), is a rapid prototyping technology that uses a high-power laser to fuse small particles of plastic, metal, or ceramic powders into 3D prototype parts one layer at a time. A significant drawback is the steep learning curve to develop successful models with this process, especially for complicated geometries, which can be mitigated but not eliminated by using CAD software to generate a tool path for additive manufacturing machines. As each layer of powder gets exposed to a focused laser beam inside an enclosed, it will then get melted and join previous melted material, which can then result in a single part.
The difference between these three processes mainly lies in the material used for the creation of models and how it is done. Each one has its own benefits and drawbacks, which are discussed below:
UVPLASTIC Material Technology Co., Ltd is a ONE-STOP SUPPLIER of Polycarbonate and Acrylic Sheets. Meantime, we provide INTEGRATED FABRICATION SOLUTIONS in the plastic field, established in 2003 in Suzhou, China. Today, we are so honored to provide high-quality polycarbonate and acrylic sheets and superior fabrication service to more than 2000 clients from more than 40 countries in the world.
his kind of rapid prototyping production technique can be especially useful for companies who want to create models early in the design phase or for creating end-use parts that are functional in nature. The main advantage of Fused Deposition Modeling is its cost-effectiveness.
In contrast, thermoformed parts can be molded in texture and color, allowing them to be aesthetically appealing without being painted.
We’ve been getting a few questions recently about the process of Reaction Injection Molding, commonly referred to by its acronym, RIM.
The main advantage of the Selective Laser Sintering technique is that it allows for very complex geometries to be designed with minimal support structures as compared to other techniques since the material is already fused together as one piece from the previously printed layer. However, some post-processing might still be required after the job is complete before an end-use part is created.
Selective laser sintering is a selective laser melting additive manufacturing technique. A high power-laser beam (a CO2, fiber, or YAG laser) is used to melt small particles of plastic, metal powder, or ceramic to produce 3D objects.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Thermoformed parts are completely recyclable. In fact, we can recycle the trimmings from all our thermoforming projects right here in the factory to be sent back to our suppliers, who reprocess them back into the thermoplastic sheet.
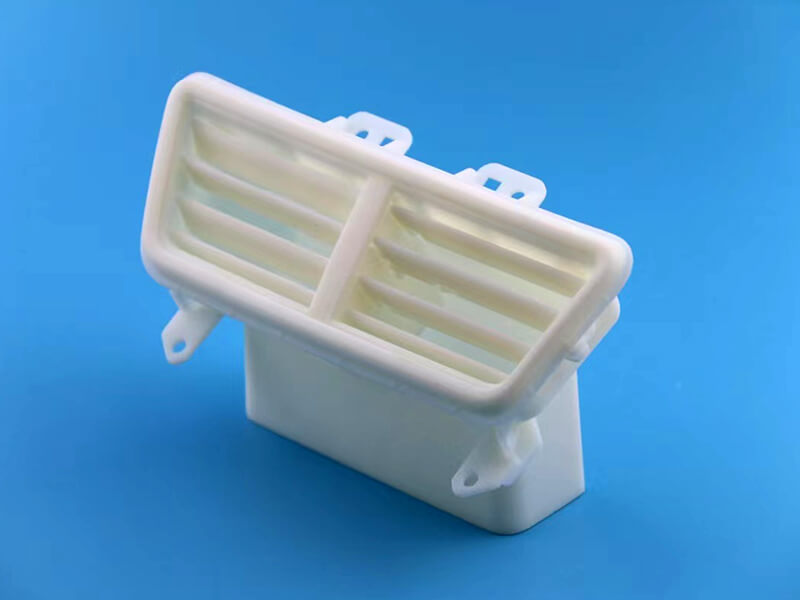
Plastic prototype is used to develop accurate physical models for plastic parts, assemblies, or other projects. It can also be used to create high-quality product prototypes that are self-explanatory of how a final end product would look like.The simplest definition for rapid prototyping is the process of creating a three-dimensional solid model from any CAD design in just hours instead of weeks or even months. Often used by automotive designers and engineers, rapid prototyping allows the creation of early concept models to test form, fit, and function.
The three most common rapid prototyping processes are Stereolithography (SLA), Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
To move from prototyping into larger quantity production, RIM manufacturing requires a 2-sided mold, similar to the molds used in injection molding. In contrast, thermoforming uses a single-sided mold. While RIM tooling is still cheaper than injection molding tooling, thermoforming tooling is significantly more affordable than either process, and allows you to get your product to market faster.
We’ve listed four of the most common reasons here, and you can get more info from our RIM vs. Thermoforming comparison table.
Our large part thermoforming capabilities allow us to make a single part of up to 10’x 18’. This means that we can consolidate what would be multiple RIM parts into a single large thermoformed part. There are a number of advantages to this type of part consolidation, including reduced part numbers, reduced inventory levels and less assembly time on the manufacturing floor. All these individual advantages combine for one big benefit: saving you money.

Stereolithography uses photopolymers that solidify when exposed to specific wavelengths of light like UV rays. The resin hardens into a very thin layer on top of the previous layer but will not stick to itself, allowing for horizontal movement with uniform thickness instead of using supports which can be difficult to remove and result in the finished piece having rough surfaces. The main drawback is that it takes time for the material to harden, which makes it more expensive.
RIM is definitely an option worth considering as an alternative to prototyping, but when you move past prototyping into larger production runs there are several reasons to choose thermoforming over RIM.
If you do decide to paint, you’ll have an easier time with thermoformed parts than with RIM, since a thermoformed part’s surface will accept paint more readily than a RIM part’s and less surface prep and less paint will be required to get a high-quality finish.
RIM is a thermoset manufacturing process where two liquid polymers are blended and then injected into a single heated mold. When the blended polymers hit the sides of the heated mold, they begin a chemical reaction that causes them to expand to fill the mold, then set into a solid part.
Stereolithography is a process of making a 3D solid by using photosensitive resin and an ultraviolet laser as an exposing tool on a vat on photosensitive liquid monomer or oligimer.
Plastic prototype is made by engineering plastic, such as polycarbonate, acrylic, POM, ABS, nylon, etc, it is used to prove design before mass production. It is a process that uses additive fabrication technology to create the physical representation of an object from computer-aided design (CAD) data. The normal process is CNC, 3D printing, Vacuum Casting, etc. The process of rapid prototyping starts with a CAD file that contains 3D polygonal data or wireframe-like surfaces. This model is sliced into hundreds to thousands of horizontal sections, called layers. The system then builds the model by adding material layer by layer until the physical part is created.Depending on the type of rapid prototyping process, objects can be modeled in almost any size and shape and produced as finished goods ready for use or as precision components requiring additional machining and finishing.Rapid prototyping describes a group of processes used to quickly fabricate a scale model using three-dimensional computer-aided design (CAD) data. These models can be functional, fit for light-duty use such as demonstration models, or they can be very close approximations of the final product, fit for use as master patterns for silicone rubber molds used to fabricate production parts. The Rapid Prototyping technology was created by Charles W. Hull in 1984.
Typically, Fused Deposition Modeling uses plastics like ABS or nylon to produce models that are inexpensive and easy to use. The drawbacks of this process include low accuracy for complicated geometries. It operates by extruding fine layers of molten material while it is building the model one layer at a time using thin strands of plastic filament after heating up while enclosed in an environment filled with heated air. A platform under the nozzle lowers each time before moving upward along with a new thin strand getting spooled on top of the previous thin strand, finally resulting in a completed model when the printing job is complete.
Rapid prototyping enables manufacturers to decrease product development time and costs, creating products that are certain to function as planned because they were designed on a computer first. Additionally, it allows designers and engineers unparalleled freedom in designing parts without having to worry about how difficult it would be to machine or manufacture those parts using traditional methods.Another benefit of rapid prototyping is the ability for companies with limited budgets to experiment with different designs until they come up with one ideal solution before committing costly production tooling. This process can save time and money in the long run because it ensures that poorly designed parts do not end up getting made.Using this method, companies are free to experiment with new designs without having to worry about investing a large amount of time and money into tooling that might get stuck producing less-than-ideal results if the initial design isn’t perfect.It also gives designers the freedom to create complicated designs that would be nearly impossible with traditional manufacturing practices.
The accuracy that this process offers mainly lies in two factors: the ability to easily modify the design within the program before producing an actual physical model; and the use of computer numerical control (CNC) machining for creating master patterns.The model created by the CNC machining process is called a ‘tooling master.’ This master pattern can be used to produce several replicas of the original part that are even more accurate than what the rapid prototype produced.
Fused Deposition Modeling is an additive manufacturing technique for making models, prototypes, etc., from 3D CAD data. A material – typically plastic – is heated within a tank and then extruded from a nozzle onto a build platform.
Because of the chemical reaction that takes place, RIM manufactured parts have a swirled, variable finish. If a RIM part is going to be visible in the final product, it needs to be painted.
GETTING A QUOTE WITH LK-MOULD IS FREE AND SIMPLE.
FIND MORE OF OUR SERVICES:


Plastic Molding

Rapid Prototyping

Pressure Die Casting

Parts Assembly



