
Interlocking Plastic Moulds Manufacturer from New Delhi - paver plastic mould
Author:gly Date: 2024-10-15
We hope that this article has given you a solid understanding of plastic rapid prototyping processes. It is crucial for both the manufacturer and the client to learn about the features, advantages, and usage of their product globally. By choosing the best prototyping method and service provider, we can improve our product in line with how quickly the world is changing.
This particular kind of plastic is the one that is most usually used. The key feature that sets them apart from thermosets is their capacity for several melt and solidification cycles. It can be heated to change its shape or geometric properties. The technique results in no chemical bonding, therefore, recycling or melting thermoplastics is a possibility.
After checking the prototypes, the designer and client can more precisely assess the outcome. That’s why we need to make plastic prototypes.
Businesses and entrepreneurs may benefit significantly from prototyping. It is a method of testing your concept before moving forward with large-scale manufacturing. Additionally, it enables the designer to present his idea to potential investors.
General Purpose ABS offers versatility and reliability. With its good impact resistance and moldability, it’s suitable for a wide range of industries. Whether it’s injection moulding, extrusion, or thermoforming, this type of ABS can handle it all. Manufacturers favor it for appliances, electronics, and automotive components due to its cost-effectiveness and consistent performance.
Time is an essential factor when performing plastic prototyping. Post-processing and assembling parts from low-quality prototypes will take longer than from high-quality prototypes.
ABS plastic material holds significance in the medical field, where precision and reliability are paramount. In this industry, ABS uses include the manufacturing of medical instrument housings, laboratory apparatus, equipment casings, and disposable syringes, among others. The material’s durability, chemical resistance, and ease of sterilization make it indispensable for medical applications.
Because larger parts take longer to print than smaller ones, the component volume also affects the cost of additive manufacturing. While some processes need a lot of labor and have high unit costs, other methods are significantly more productive and cost-effective.
Therefore, if you are a skilled independent businessperson and can make a prototype by hand, it will only cost you in terms of time and materials.
After treatment of condensation polymerization, they are also referred to as thermosets and show the primary bond between molecular chains. In thermosetting materials, polymers undergo another process known as healing, which is triggered by heat, light, or other suitable radiation. Thermosetting polymers do not melt when heated; instead, they break down and do not reform when cooled. Thermosets cannot be recycled or converted back into their original component.
Manufacturers can swiftly make a high-quality product thanks to injection molding. It works well for extremely small manufacturing runs. You don’t have to compromise product quality in the process of manufacturing. It helps you determine what you need for a full production run.
ABS plastic is highly valued in various industries due to its exceptional mechanical properties. Additionally, its resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion enhances its appeal. In fact, ABS’s remarkable impact resistance and toughness also make it essential for applications demanding strength and durability, including automotive components and household appliances.
With the growing complexity of product manufacturing, selecting the right materials is crucial for any product’s success. Due to this reason, ABS plastic, short for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a popular material considered widely for its versatility and dependability.
Plating Grade ABS is all about aesthetics and surface quality. With special additives for light stabilization and modification, it provides a smooth and pristine finish. This type of ABS is highly sought after in industries where appearance matters, like electronics, telecommunications, and automotive sectors. Its compatibility with plating processes ensures that the final products look polished and professional.
The durability and impact resistance of ABS plastic makes it a popular choice for crafting toys and games. Its ability to be molded into intricate shapes further enhances its appeal in this industry, ensuring that products can withstand rough play and maintain their integrity over time.
Extrusion: ABS is extruded into tubes, rods, or sheets by pushing molten material through a die. It’s versatile and efficient for various applications.
The method of efficiently manufacturing products is called rapid prototyping. Rapid prototyping is a tool engineers and product designers use for all types of product development. It is a paid professional service.
A product’s usability and popularity among customers are improved by strategically placing interface elements.Prototyping also helps to save a lot of time. Additionally, it facilitates the design creation process, and during the prototyping phase, it is easy to spot extraneous components that are best left out. The workload of the designer during the manufacturing process is greatly reduced by this technique, ultimately resulting in cost savings for the client.
Blow Molding: Blow molding shapes hollow ABS parts by inflating molten plastic in a mold cavity. It’s efficient for large volumes of lightweight products.
When designing and manufacturing products using ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), it’s crucial to prioritize sustainability and consider the environmental impact at every stage of the process.
When it comes to household appliances, ABS plastic uses are common in this industry too. From vacuum cleaners and blenders to coffee makers and kitchen utensils, ABS material finds applications in various household items. Its robustness, chemical resistance, and ease of processing make it a preferred choice for manufacturers in this sector.
Are you curious to know what ABS plastic is used for? Well, ABS plastic finds extensive use in diverse industries, contributing to the production of a wide array of products tailored to meet specific needs. Let’s explore some common industries in which ABS plastic uses are common.
This blog post aims to explore five different methods for manufacturing plastic prototypes, highlighting the advantages and limitations of each method.
High-quality ABS plastic comes in various grades, each designed for specific applications. Here’s a breakdown of the different types:
High-quality ABS plastic parts can be manufactured using various processes tailored to different production needs and design requirements. This includes ABS injection molding and various other machining processes, each catering to different design and production needs.
This plastic CNC machining technique is incredibly adaptable and practical for a wide range of product sizes, complexity, and threaded features, and it is especially well-suited to prototypes that need to meet strict tolerance requirements.
Through the use of a plastic injection mold prototype, you may see a practically identical development of your finished product in reality. Many companies, including those in the automotive, electronic, healthcare, and packaging sectors, often use this strategy. It works effectively for items that need a lot of testing and certification.
Furthermore, it offers the advantage of recyclability, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainability in manufacturing. Despite its numerous benefits, ABS plastic does have limitations, such as its relatively low melting point and vulnerability to UV radiation.
Another great technique for making plastic prototype components swiftly is injection molding. The procedure begins with the construction of an aluminum or steel mold equipped with a runner system, a channel that allows molten plastic to flow to the chamber of the mold. The required plastic prototype is created by injecting molten plastic ingredients into the mold, allowing them to cool and solidifying them.
With multiple options present, it’s important to understand what they are and how they work to choose the most suitable method for your projects. Hence, let’s go ahead and explore the most popular manufacturing processes considered for ABS plastic manufacturing and why are ideal.
Injection Molding: This method injects molten ABS into a mold cavity, forming intricate parts for mass production. It’s ideal for complex geometries and ensures consistent quality.
The material’s good abrasion resistance enhances its longevity, making it suitable for applications subject to frequent friction or movement. Moreover, ABS polymer’s structural sturdiness ensures it can withstand mechanical stresses, reinforcing its applicability across systemic applications like aerospace and construction that demand a robust material.
When it comes to understanding what is ABS plastic, this specific plastic is a composition of three primary monomers as shown in the table below: Acrylonitrile, Butadiene, and Styrene. Each monomer contributes distinct properties to the overall composition of ABS, resulting in its unique characteristics.
Plastic ABS plays a key role in the automotive industry, serving as a cornerstone for various interior and exterior components. From dashboards and instrument panels to door panels and trim, ABS finds its place in various automotive parts. Its strength, impact resistance, and impeccable surface finish make it indispensable in the automotive sector.
Vacuum casting would produce components that are almost comparable to those of injection molding and may be utilized without post-processing, but alternative procedures, like 3D printing, may require some post-processing time but are considerably more versatile for complex shapes.
Additionally, prototyping is a crucial step in the creation of a product. A CAD model is a computer-generated illustration of your concept. Using a CAD model, you may evaluate how your prototype or model will fit together. It will also demonstrate how your product will work, which is more important.
Starting with the consumer electronics industry, ABS plastic material is a go-to choice for crafting computer keyboards, mice, remote controls, phone cases, and housings for audio/video equipment. Its blend of impact resistance, versatility, and electrical insulation ABS properties makes it ideal for these applications, ensuring durability and reliability.
Numerous varieties of plastic are available for 3D printing, each with unique qualities that make it best suited for particular situations. The main categories of plastics used in 3D printing are described as follows:
Now that we know the common uses of ABS plastic, it’s important to understand the additional ways ABS can be used for design and production needs. This refers to the modification of plastic ABS materials by blending them with some common polymers to enhance the specific properties of a product by combining polymer properties with the balanced properties of ABS. Some such common modifications include:
Vacuum casting involves first creating a master pattern of the desired part using 3D printing or CNC machining. This pattern is then used to make a silicone mold.
So, what is ABS material? ABS plastic material, an acronym for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, presents a versatile and eco-friendly option for manufacturers. Comprising three key monomers – Acrylonitrile, Butadiene, and Styrene – ABS combines high chemical resistance, toughness, and rigidity, making it a preferred choice across industries.
As shared earlier, some of these alternative materials are modified with ABS to enhance their balanced properties. But when it comes to independent product choice, ABS is always a more balanced product option for specific product manufacturing needs of designers and manufacturers.
Next, a two-part liquid material such as polyurethane or epoxy resin is poured into the mold cavity. The mold is placed in a vacuum chamber, where the air is removed, creating a vacuum that forces the liquid material into the mold’s cavities and ensures the part is free from air bubbles or voids.
Nevertheless, high-quality ABS remains a top choice for manufacturers and designers seeking a cost-effective, durable, and versatile material for their products, continuing to meet the demands of various applications effectively.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a novice in the field, this post will provide you with valuable insights into the world of plastic prototype manufacturing and help you make informed decisions about which method to choose for your project.
By adding CAM software to the process, manufacturers can fully automate it. Plastic pieces may be machined at a reasonable price, and the whole process takes minimal time. CAD rendering is all you need to get started with CNC plastic prototyping.
How exactly? Let’s explore by comparing ABS with other alternatives that are commonly considered for product design and manufacturing needs.

To help you better understand this popular plastic, this detailed ABS plastic guide will explore all that and more. So keep reading to learn all about it!
4. ABS+PA (Nylon): Automotive engine components like engine covers, intake manifolds, and other under-the-hood components are manufactured with ABS blended with polyamide (PA). The combined properties of ABS and PA add to the mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability of these products, making them suitable for demanding engineering applications.
ABS exhibits remarkable resistance to impact, even in low-temperature conditions, making it highly versatile for environments experiencing significant temperature fluctuations. Its inherent rigidness and strength make it ideal for applications requiring structural integrity, such as drones and rockets, where weaker materials might fail under stress or load.
This polymer maintains consistent mechanical strength and stability over time and under various conditions, reinforcing its suitability for long-term applications. Additionally, ABS is known for its exceptional weldability, facilitating the efficient joining of parts in ABS plastic manufacturing and construction processes, thus enhancing productivity.
Thanks to 3D printing, you may swiftly and effectively create parts for various applications. By using the appropriate 3D printing method and material combination, you may produce things with the desired mechanical properties, functional attributes, or aesthetics.
The software needed to print prototypes is often exclusive to the hardware utilized; nonetheless, the following list of CAD applications is used to produce models:
In certain cases, a quick prototyping industry will simply require an initial design to start the production process and create a computer model. OEMs (original equipment manufacturers) that want a high-quality prototype quickly and have the financial means to do so may consider using rapid prototyping.
Rapid prototyping is appropriate for plastic products that must have an exact dimension or fit. Engineers and product designers sometimes have to test the plastic prototype several times quickly to fulfill deadlines to attain perfection. As the name says, rapid prototyping has this benefit.
1. ABS+ASA: Products manufactured with ABS combined with acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA) offer improved weather resistance, UV stability, and color retention, making it suitable for outdoor applications. As an example, chairs and tables made from ABS+ASA blend are weather-resistant, and UV-stable. This type of furniture also retains its color even after prolonged exposure to sunlight, making it ideal for outdoor use.
2. ABS+PMMA: ABS products blended with polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) provide enhanced transparency, gloss, and scratch resistance. This makes it ideal for manufacturing products like light diffusers and transparent lamp covers with applications that require clear or transparent parts.
3. ABS+TPE: ABS combined with thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) improves flexibility, impact resistance, and soft-touch properties, making it suitable for applications where rubber-like flexibility is required. Common examples of this can be phone cases as well as grips of handheld tools.
CNC Machining: CNC machining shapes ABS material through milling or turning operations. This process is flexible for low-volume or customized parts with precise details.
The process of CNC machining is subtractive. In other words, it entails removing material from an unfinished item. A milling machine is used to do CNC machining on plastic components. A milling machine has many axes that may be manipulated.
What kind of technique and post-processing you need will depend on how accurately the final product must be produced. You should also think about how well your prototype compares to your finished product in terms of quality. Rapid plastic prototyping techniques provide prototype items with a high-quality surface finish.
When choosing a prototype option, cost is always an important factor to take into account. The quantity of prototype components needed is essential in determining the procedure since some prototyping methods are only financially viable for lesser numbers.
This plastic stands out as an optimal material for a diverse array of systemic applications, thanks to its multifaceted attributes. Let’s delve into some of the key ABS properties, shedding light on why it’s a preferred choice across various industries.
3D Printing: 3D printing builds ABS parts layer by layer from digital models. The 3d printing production process is cost-effective and suitable for rapid prototyping with complex shapes.
High-impact ABS stands out for its durability and toughness. By incorporating fillers or rubber modifiers, it becomes exceptionally resistant to impacts and deformation. This type of ABS is popular in applications where strength and crack resistance are crucial, such as electronics, automotive parts, and toys. Its ability to withstand rough handling makes it a top choice for various products.

Did you know that the addition of butadiene in the 1950s significantly improved plastic ABS’s processability and toughness, making it commercially viable? In terms of density, it is approximately 1.05 g/cm³ dense and exhibits rigidity, strength, and chemical resistance, although it’s sensitive to polar solvents.
Thermoforming: Thermoforming heats ABS sheets, molds them, and cools them to shape parts. This production process is commonly used for packaging and automotive components.
While there are several alternative materials available for various applications, ABS stands out as a versatile option with balanced properties suitable for a wide range of general-purpose parts, enclosures, and housings.
High-quality ABS plastic exhibits remarkable resilience to alkalis and diluted acids, ensuring the longevity and reliability of products exposed to such chemicals.
One of the most expedient ways to produce plastic prototypes is through CNC precision machining. CNC machines use a range of cutting tools and cutter paths that are specially designed for the desired cut when carving a 3D model directly from a solid block of plastic.
High-flow ABS is all about fluidity and ease of processing. Thanks to its unique formulation with higher molecular weight styrene monomers, it flows smoothly during molding and shaping. This makes it perfect for creating intricate designs and thin-walled parts. Manufacturers often use high-flow ABS in painting and industrial processing applications, where precision is paramount.
ABS plastic material contributes to the manufacturing of sports and recreation equipment, ensuring safety and durability in various activities. From helmets and protective gear to athletic equipment and bicycles, ABS material’s impact resistance and ability to withstand outdoor conditions make it an ideal choice for sports enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Specifically, designers and manufacturers broadly consider this material for its impact resistance, toughness, and lightweight nature. Its versatility further makes ABS machining, molding, and fabrication easier, making it a more suitable manufacturing material across multiple industries.
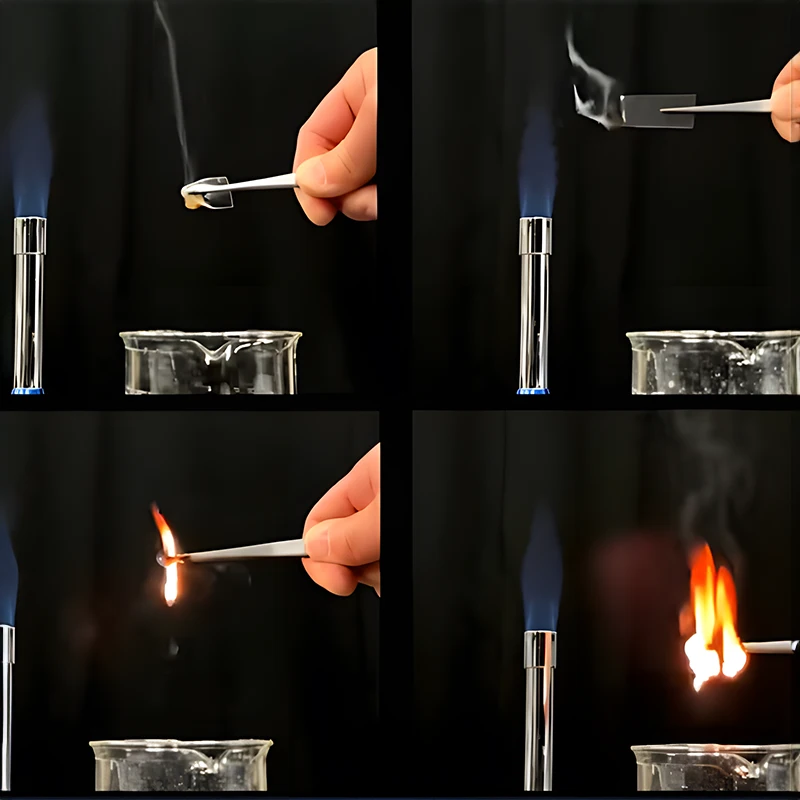
The material greatly influences the quality of the prototype. Selecting components made via additive manufacturing may not be the best option if functional features are connected to unique material qualities, such as surface polish and durability. Following are a few examples of common plastic materials used in various industrial processes:
While it demonstrates moderate resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons, careful consideration is needed for applications involving alcohols, hydrocarbons, and halogenated hydrocarbons due to its limited resistance to these substances.
In today’s fast-paced world, product development is becoming more competitive than ever. In order to stay ahead of the competition, engineers and designers must be able to produce high-quality plastic prototypes quickly and efficiently.
Flame Retardant ABS takes safety to the next level. By incorporating flame retardants, it prevents ignition and reduces the risk of fire hazards. This type of ABS is indispensable in environments where electrical insulation and flame resistance are non-negotiable, such as electrical device housings. Its ability to withstand high temperatures makes it a reliable choice for critical applications.
The use of rapid prototyping technologies during the production process guarantees a high degree of precision and accuracy. It is fair to believe that design drawings of CAD software are quite accurate. Precision is a crucial component to take into account since it guarantees that your product will be produced consistently.
Since there are some methods to get the desired objective, each has its unique benefits and drawbacks that should be considered. How to choose the suitable one? Continue to read!
Despite its popularity, understanding the properties is crucial for designers and manufacturers seeking to leverage its full potential. It is also important to understand the wide industrial applications, manufacturing processes, how ABS differs from alternative materials, and the different processes you can consider for ABS plastic manufacturing.
Additionally, a prototype using this technique will enable you to test every component you want. Additionally, it will serve as the basis for the succeeding mold that will be used for your whole manufacturing process.
Making prototypes before starting full-scale production of your items might be highly beneficial. The industrial sector has benefited from prototyping improvements by quickly producing plastic prototypes.
ABS boasts commendable insulating properties, making it a reliable choice for electrical or thermal insulation applications, ensuring safety and efficiency. Its outstanding surface brightness meets both functional requirements and aesthetic considerations, making it an excellent choice for industrial and consumer-facing products alike.
GETTING A QUOTE WITH LK-MOULD IS FREE AND SIMPLE.
FIND MORE OF OUR SERVICES:


Plastic Molding

Rapid Prototyping

Pressure Die Casting

Parts Assembly



